Netskope Threat Research Labs has detected a new strain of the Zepto ransomware shared among cloud users. As has been the trend in recent months, this strain of Zepto arrives at its destination via spam emails that use enticing messages and filenames to encourage the recipient to open the email and download the infected file. These files use an extension of .wsf, which causes Windows to assign an icon that appears similar to a spreadsheet icon. This icon, coupled with a filename of spreadsheet_286..wsf may cause all but the most attentive recipient to view the attachment as legitimate. These messages are then shared among colleagues using cloud SaaS applications such as Microsoft OneDrive, Google Drive, Box, Dropbox, etc.
We have observed sharing and collaboration in cloud apps to represent an often ill-considered secondary propagation vector for malware. Once the spreadsheet_286..wsf file is shared in the cloud, share recipients could easily assume that this “spreadsheet” originated locally and was legitimate, causing the malware to be executed within the protected domain.
Zepto has been observed spreading through “.wsf” (Windows Script File) files within the archive unlike regular JavaScript files. Upon execution, the Windows Script File is executed by Microsoft Windows Script Host which allows mixing the scripting languages JScript and VBScript within a single file. This interlacing of languages permits the attacker to evade detection engines reliant upon emulation of one language.
Netskope Active Threat Protection detected a zip file being shared on Microsoft OneDrive containing a malicious script file with .WSF (Windows Script File) extension. As shown in Figure 1, this WSF file was named spreadsheet_286 with two “.” s in the extension.
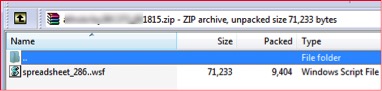 Figure 1: Zip attachment with .wsf file inside
Figure 1: Zip attachment with .wsf file inside
The script file starts with <job>tag and is heavily obfuscated. The obfuscated JavaScript code is shown in Figure 2 below:
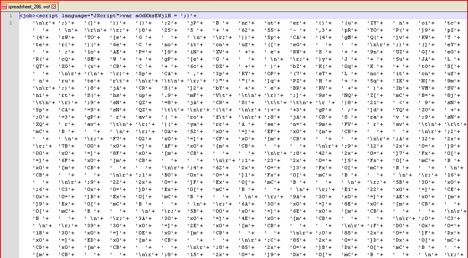
Figure 2: Obfuscated WSF script code
Once the WSF script is de-obfuscated, the outer layer code looks as shown in Figure 3 below.
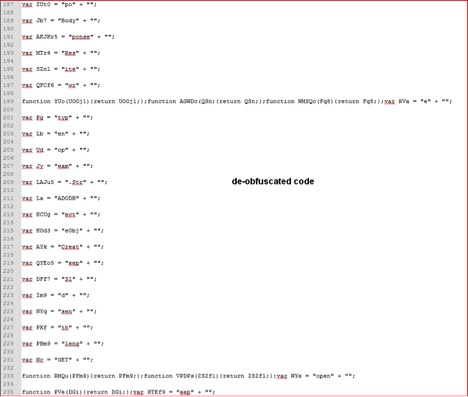
Figure 3: De-obfuscated script code
The script is again encoded using string substitution encoding, where strings are split into multiple variables. The above decoded script has many interesting strings being broken into different variables just to make manual analysis more difficult. By looking at the interesting variables with strings like “http” we are able to echo those variables using “WScript.Echo()” to understand behavior of this script. A closer look at the de-obfuscated code reveals some interesting variables as shown in Figure 4 below:
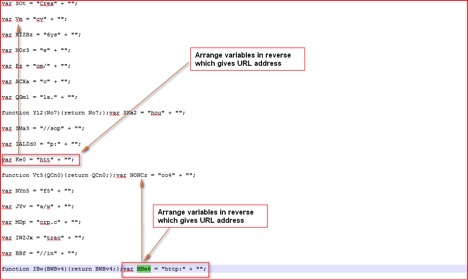 Figure 4: URLs split into different variables
Figure 4: URLs split into different variables
The URLs are split into different named variables and we can find references to these variables in our script as shown in Figure 5 below:
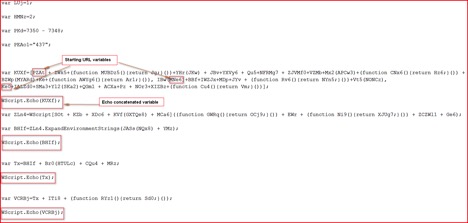 Figure 5: URL variables concatenated into one variable
Figure 5: URL variables concatenated into one variable
Once we echo interesting variables, the script reveals its malicious purpose as shown in Figure 6 & 7 below:
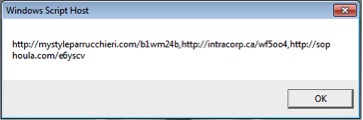 Figure 6: Compromised domains list
Figure 6: Compromised domains list
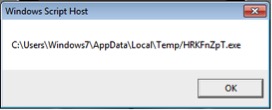 Figure 7: Temp file name for Zepto
Figure 7: Temp file name for Zepto
As shown above, the script will download the main payload of Zepto which is in custom encrypted format from any of these 3 compromised domains, decrypt it using code shown in Figure 8 below, performs some validity checks and will save that under %TEMP% folder with name “HRKFnZpT.exe” to execute it later. The DecryptFile code after some string substitutions is shown in Figure 8 below:
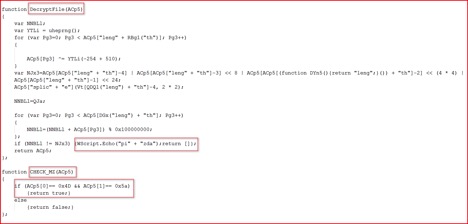
Figure 8: DecryptFile code and MZ file Check code
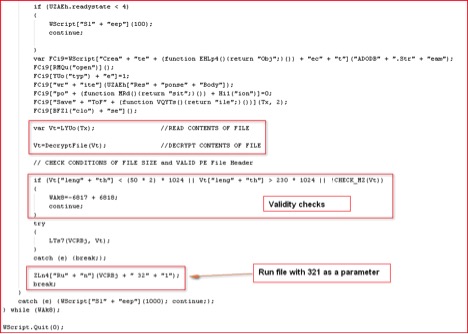
Figure 9: Script routine to execute malicious Zepto payload
The Zepto will only run its main payload if the correct parameter “321” is supplied. This is quite similar to the way Locky ransomware executes its payload. The script routine to execute the payload is shown in Figure 9. This sample didn’t execute under VMware even after correct parameter was supplied to the script. It suggests the presence of anti-VM checks inside the binary. After opening it under OllyDbg, we found several calls to RDTSC (Read Time Stamp Counter) assembly instructions as shown in Figure 10 below:
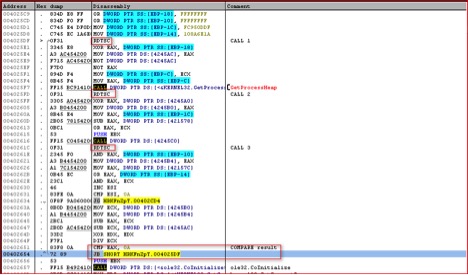
Figure 10: Calls to RDTSC instructions
Once we bypass this anti-VM checks, the malicious Zepto payload executes itself. It collects system information and sends it across to the attackers IP as shown in Figure 11 below:
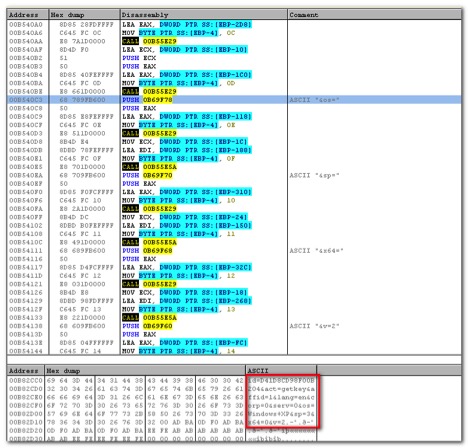
Figure 11: System data to be sent over network before encryption
The above information is encrypted and sent to “upload/_dispatch.php” of hard-coded IP addresses as shown in Figure 12 and 13 below:

Figure 12: Hard-coded IP list and PHP file path
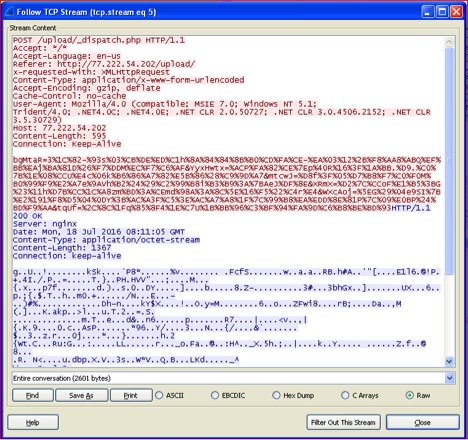
Figure 13: Network traffic sent to Zepto C&C
Once the information is sent to Zepto’s C&C server, it will respond back with the RSA key that is used for encryption. The response itself is encrypted as seen in Figure 13 above. The decrypted response is shown in Figure 14 below:
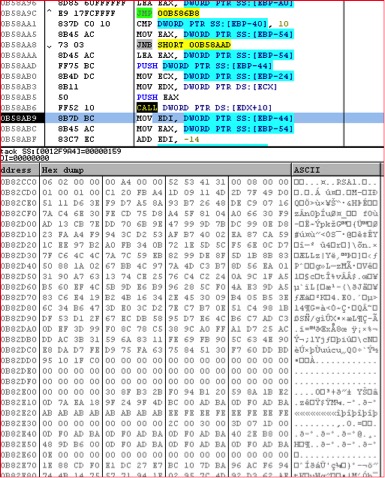
Figure 14: Decrypted first response from C&C
Zepto will use the RSA key and start encrypting files (excluding Windows and System files) with a “.zepto” extension and also the Victim ID as the filename prefix as shown in Figure 15 below:
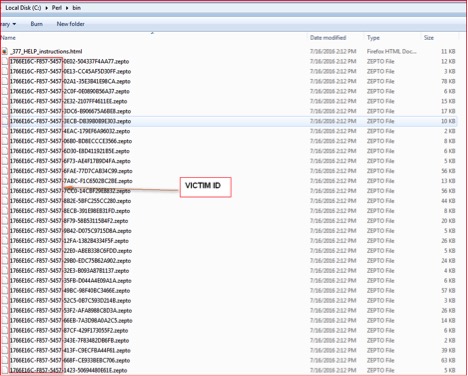
Figure 15: Encrypted files with .zepto extensions
It will drop two files on the desktop of the victim named “_HELP_instructions.bmp” and “_HELP_instructions.html”. It will open a ransom warning page and set it as the desktop’s wallpaper. The ransom notes are shown in Figure 16 & 17.
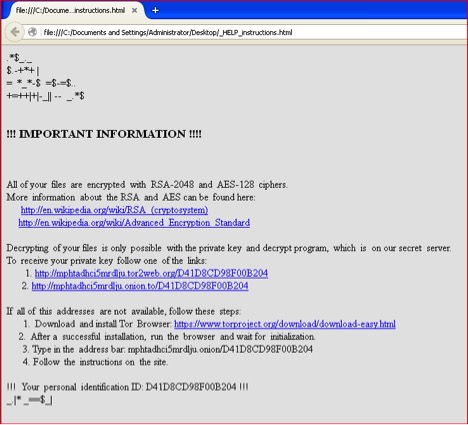
Figure 16: Zepto ransom warning HTML page
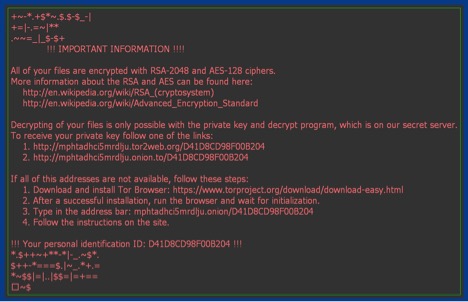
Figure 17: Zepto ransom warning wallpaper
Zepto encrypts all the files that match the file extensions shown in Figure 18 below:

Figure 18: Zepto file extensions lists
Is Zepto using similar code to Locky?
There are a number of elements which confirm Zepto to be a slightly modified version of Locky:
- The use of the “321” parameter to run its main payload
- The use of RTDSC instructions to bypass VM
- Collecting similar system information, encryption and upload mechanism
- Similar ransom note warning and wallpaper
- Mention of the Locky decryptor on Zepto ransom page as shown in Figure 19 below:
 Figure 19: Zepto ransom payment page
Figure 19: Zepto ransom payment page - The presence of strings “_Locky_recover_instructions.bmp” and “_Locky_recover_instructions.txt” inside memory of Zepto ransomware as shown in Figure 20 below:
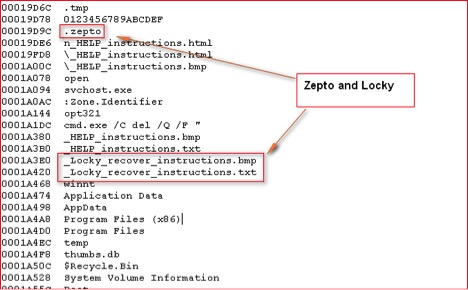
Figure 20: Memory strings inside Zepto binary
All of the above confirm that Zepto is a variant of Locky which uses “.zepto” extensions for encrypted files. Ransomware authors are very active and moving to different delivery mechanisms to bypass scanning engines.
Netskope’s Detection & Remediation
Netskope Active Threat Protection will detect this threat as “Backdoor.Backdoor.Downloadr.DPW”.
Netskope recommends that its users create a policy to block access to extensions such as .wsh, .js, and .vbs. These policy alerts will appear as follows:
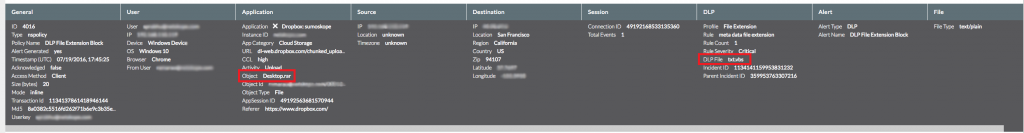
Figure 21: Netskope policy violation for sharing files of this type.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Zepto downloaded encrypted binary
MD5: 6968F0AF128C27C6C970ADC0B301D204
Main Zepto decrypted binary
MD5: 13BF5D82676026EFCF47C411D6C4429C
WSF File
MD5: 7340EFCB3B352CD228A77782C74943A4
Compromised Domains:
hxxp://mystyleparrucchieri.com/b1wm24b
hxxp://intracorp.ca/wf5oo4
hxxp://sophoula.com/e6yscv
C&C IPs:
77.222.54.202
91.209.77.166
185.118.66.83
5.187.0.137
185.5.250.135




 Back
Back














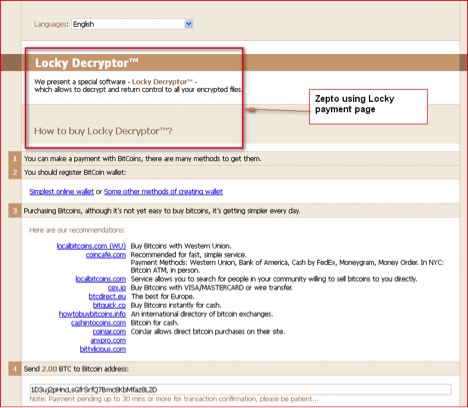 Figure 19: Zepto ransom payment page
Figure 19: Zepto ransom payment page
 Read the blog
Read the blog